51170
•
10-minute read

SEO in 2025 looks very different from just a few years ago. With Google AI Overviews answering broad queries directly in search, relying only on high-volume “head” keywords has become less effective. To stand out, marketers are turning to long-tail keywords — highly specific search phrases that capture intent Google can’t fully satisfy in an AI box.
Long-tail keywords may not bring thousands of clicks each, but together they drive the majority of Google searches. More importantly, these queries connect you with people who are closer to making a decision — whether it’s buying a product, booking a service, or clicking on your ad.
In this guide, you’ll learn:
What long-tail keywords are (with fresh 2025 examples).
Why they’re critical for SEO, PPC, and local businesses.
How to find and create long-tail keyword phrases using free and paid tools.
How to optimize your website content for long-tail searches.
By the end, you’ll know how to use long-tail keywords strategically to grow organic traffic, lower PPC costs, and improve conversions — even in the era of Google AI Overviews.
A long-tail keyword (also called a long tail keyword phrase) is a highly specific search query, usually three or more words long, that targets niche intent. Unlike short, generic keywords (“shoes”), long-tail focus keywords such as “waterproof hiking shoes for women” attract fewer searches but bring visitors who are closer to converting.
The name “long-tail” comes from the search demand curve: a small set of high-volume keywords sits at the “head,” while the “tail” contains millions of low-volume queries. Taken together, these long-tail keywords account for the majority of searches on Google.
Because of their specificity, long-tail keywords are easier to rank for and often deliver higher conversion rates than broad terms. They’re also becoming increasingly important with voice search and Google AI Overviews, where people type or speak queries in natural, conversational language.
Example: Instead of searching “SEO tools,” someone might search “best SEO tools for long tail keyword research in 2025.”
Long-tail keywords are best understood through examples. A long tail keyword phrase usually extends a generic term with details about intent, location, or audience.
Here’s how short-tail and long-tail focus keywords compare:
| Short-tail keyword | Long-tail keyword phrase | Search intent |
|---|---|---|
| shoes | waterproof trail running shoes for women | Ready to buy, product-focused |
| dentist | affordable pediatric dentist near me | Local service, urgent need |
| SEO tools | google long tail keywords research tool | B2B, problem-solving |
| gym workout | 4-week strength training program for beginners | Informational, step-by-step |
| buy laptop | best gaming laptops under $1500 in 2025 | High purchase intent |
Of course, the length of the search phrase is just a rule of thumb. In reality, long-tail keywords are named this way not because they are long, but because they come from the long tail of the search volume curve:
Notice how longtail keyword phrases capture what people actually type into Google: they’re longer, more natural, and often mirror spoken queries.
Pro tip: when creating long-tail keywords for your website, think about the who, what, where, and when behind a search. For example:
“best Italian restaurant open late in Brooklyn” (who + where).
“how to use long tail keywords in Google Ads” (what + tool).
“SEO software for startups in 2025” (who + when).
This level of detail makes your content more likely to rank, attract the right visitors, and even appear in AI Overviews.
Imagine you run a business that sells furniture. Competing for a broad term like “furniture” is nearly impossible, especially if you’re a small company without the authority of giant retailers. However, if you specialize in something more niche—say contemporary art-deco pieces—you can target precise searches like “contemporary art deco semi-circle lounge chair.” That phrase won’t attract millions of searchers, but the people who type it in are already looking for exactly what you sell.
That’s the strength of long-tail keywords: they connect your products and services to people who are already motivated to buy.
Think of the difference between someone typing “sofa” versus “elm wood veneer daybed.” The first searcher is browsing, possibly at the very start of their journey. The second knows exactly what they want—and is far more likely to make a purchase quickly.
Yes, long-tail keywords bring in less traffic than broad “head terms.” But the visitors you do attract tend to be more focused, more motivated, and more ready to convert into customers.
The phrase “long tail” comes from the shape of a demand curve. If you graphed keyword popularity across the web, a handful of terms—think “Facebook” or “Taylor Swift”—would dominate the front of the curve. These are the high-volume “head” keywords.
Here’s the surprising part: those ultra-popular terms only represent about 10–15% of total searches. Mid-length queries make up another 15–20%. The rest—roughly 70% of searches—are distributed across countless unique, lower-volume phrases. That’s the “tail” of the curve, stretching endlessly with millions of variations.
For marketers, this means the real opportunity lies not in chasing the head terms, but in harnessing the collective power of long-tail keywords.
We've analyzed 24 million keywords from our database to learn more about the role of long-tail keywords in search. The first thing we've looked at was keyword diversity. Turns out, short tail (one- and two-word) queries comprise only a quarter of our database, while the majority of our database consists of long tail (three-, four-, and five-word) queries:
But the situation is very different when we look at search volumes, which you cannot ignore when it comes to SEO. Here, we can see that one- and two-word keywords pull over 65% of all search volume. And the search volume drops dramatically as keywords grow longer:
Lastly, we've looked at the distribution of keywords by the number of searches. Turns out, over 80% of queries are searched fewer than 10 times per month.
In 2025, long-tail keywords are more important than ever. Google’s AI Overviews often answer broad, short-tail searches directly in the results page — leaving little organic traffic for websites. But when users search for long-tail keywords with specific details or intent, AI often can’t provide a complete answer. That’s where optimized pages still win clicks.
Target and focus more on answering the long tail queries of your users… We are going to see a much bigger and more important impact from those as a consequence of the AI overviews…
Several trends explain the dominance of long-tail keyword research today:
Most searches are long-tail. Studies show (including our own) that over 70% of Google queries are made up of three or more words. This means when you search for long tail keywords, you’re actually working with the majority of the search landscape.
Searches are becoming more conversational. Voice assistants and mobile devices encourage people to type or speak full questions rather than one or two words. Queries like “what is the best longtail keyword research tool for ecommerce?” are becoming the norm.
High commercial intent. Long-tail keyword research reveals terms that match purchase-ready intent, which makes them especially valuable for PPC campaigns and product pages.
Lower competition. When you find longtail keywords with low search volume, you often discover opportunities competitors ignore — a quick win for smaller websites.
Why invest time in long-tail keyword research when volumes are low? Because these terms bring the kind of traffic that matters.
Here are the biggest advantages of long tail phrases in 2025:
Generic short-tail keywords are incredibly competitive — everyone wants a piece of high traffic SERPs. But because they are so competitive, only the highest authority websites get to rank on page one. We are talking about major industry players.
If you are not a major industry player, then competing for short-tail keywords may be a waste of time. Yes, your keywords are searched thousands of times per month, but what's the point if all that traffic goes to your competitors?
To illustrate the point, I've run a short-tail, a mid-tail, and a long-tail keyword through the Rank Tracker tool and got some keyword stats. As you can see on the screenshot below, keyword difficulty drops dramatically as keywords get longer. This means that top-ranking websites have fewer backlinks, less-optimized content, and lack other signals of authority:
Download Rank TrackerAlso, long-tail terms usually relate to a much smaller niche of products and services, where it's easier for you to compete. For example, every bike store sells bikes, but not all of them sell gravel bikes. Of those that do, barely any stores sell titanium gravel bikes.
If you sell titanium gravel bikes, then this should be the keyword you optimize for first. Yes, it's searched only 1,000 times per month, but there is a good chance you'll rank on page one and get at least some of this traffic.
Users who search for more specific terms are further in their buying cycle than searchers who use generic queries. Normally, long-tail keywords have 2.5 times the conversion rate of short-tail keywords.
This makes perfect sense. Someone searching for best bikes is probably just exploring. But someone searching for best gravel bikes under $1000 has a much stronger purchase intent and is probably just a few steps away from pulling the trigger.
Optimizing for long-tail keywords does not come at a cost of short-tail keywords. It's not an either/or type of situation. In the below example, the long-tail keyword contains two shorter keywords that might be a signal for more generic searches as well. This sort of allows you to kill two birds with one stone.

Internet marketers agree that PPC (Pay Per Click) advertising should be mostly long-tail. And here is why. In PPC, you pay each time someone clicks on your ad. If you bid on non-specific, very broad terms you'll probably have many clicks, but with lower conversions. Thus, a lot of money will be wasted on ill-targeted traffic and will not bring real customers.
However, if you bid on more specific long-tail search phrases that better describe what you sell or offer, you are likely to attract just the right visitors to your site, and your PPC campaign will pay off sooner. In the end, a better exact match to queries will make advertising more cost-effective.
You must have noticed that Google is now capable of satisfying very narrow search intents. It can show a small fragment of a video as a separate search result, it can index passages, and it does a whole lot with featured snippets and other SERP enhancements. All of these features rely on long-tail keywords.
Basically, what Google needs are bite-size pieces of information optimized for long-tail queries. This way it can satisfy specific search intents quickly and efficiently:
And as content creators, we have no choice but to accommodate Google. Think of it this way. Instead of having an article loosely optimized for one keyword and a few of its variations, create an article where each segment is optimized for a particular long-tail keyword.
To give you an example of what I mean, here is a piece of text from this article:
The H2 heading for this section is a query-like keyword written in natural language. The first sentence after the heading starts with a keyword as well. And the whole paragraph is just under 40 words — the perfect length for a featured snippet.
Here is another example:
And it's the exact same thing. The H2 heading is a long-tail keyword and the paragraph is a no-nonsense answer exactly 40 words long. Now I fully expect both of these segments to be eligible for a featured snippet whenever someone uses these exact search queries.
Google increasingly surfaces passages, FAQs, and featured snippets for specific questions. Content optimized with long tail phrases is more likely to be pulled into these results.
Look at the SERPs… identify which related questions Google directly suggests within the AI overview… look for these additional inputs… that are already being referred to by Google and given visibility in the search results.
Long-tail keywords aren’t just for ecommerce or SaaS — they’re a lifeline for local businesses. In competitive local markets, ranking for broad terms like “dentist” or “pizza” is nearly impossible. But when you focus on long tail keywords for local businesses, you can capture customers who are actively looking for services nearby.
Examples of local long-tail keyword phrases:
affordable pediatric dentist in Austin open weekends
best pizza delivery near downtown Chicago
emergency plumber 24/7 in Los Angeles
dog grooming salon with mobile service in Brooklyn
These searches may only happen a few dozen times a month, but they bring in visitors with immediate intent to buy or book.
List your services and products.
Add modifiers like city, neighborhood, or “near me.”
Use a website keyword checker or related keywords generator to expand the list.
Prioritize terms with strong intent (e.g., “emergency,” “best,” “affordable”).
When you build keywords for website pages around local intent, you’ll rank higher in local packs, Google Maps, and voice search results.
Pro tip: many local searches happen on mobile. Optimizing for long-tail mobile-friendly queries such as “closest coffee shop open now” can help you capture voice searches triggered by assistants like Google Assistant or Siri.
Long-tail keywords are just as powerful in paid advertising as they are in organic SEO. In fact, for many small and mid-sized businesses, AdWords long tail keywords can make the difference between a profitable and an unprofitable campaign.
Lower CPC – Broad keywords like “insurance” or “marketing software” cost several dollars per click. Google long tail keywords such as “affordable car insurance for students in Florida” often cost far less.
Higher relevance – Ads triggered by long tail phrases are more closely aligned with user intent, which improves Quality Score.
Better ROI – Targeting long tail keywords AdWords campaigns means fewer wasted clicks and more qualified leads.
Do keyword research. Use Rank Tracker, Google Keyword Planner, or a long tail keyword tool to identify relevant phrases.
Build tightly themed ad groups. Group long tail phrases by topic (e.g., “plumber near me” keywords vs “emergency plumber”).
Write ad copy that mirrors search intent. If the keyword is “buy eco-friendly cleaning supplies online”, use that exact phrasing in your ad headline.
Optimize landing pages. Make sure the target keyword is included in headings and calls to action.
Refine with negative keywords. Exclude terms like “free,” “cheap,” or unrelated services that could drain your budget.
Pro tip: AdWords long tail keywords aren’t just for saving money — they also help you discover profitable niches you might not have targeted with SEO.
The easiest way to turn a short-tail keyword into a long-tail keyword is to google it. You can then use Google's recommendation system to find more keyword variations.
The first place to look is Google autocomplete. Just start typing your keyword and Google will suggest about a dozen of ways to finish it — those are your primary long-tail keywords:
Once you are on the search results page, you can look around for other keyword suggestions. At the top of the page there will often be a People also ask section with a few popular questions around your query:
And at the bottom of the page you will find a Related searches section with a few ways to modify your query and make it more specific:
Alternatively, you can turn to a tool that will collect this information for you. A popular option is AnswerThePublic website, where you can enter your seed query and get a list of related questions:
Of course, if you want to research long-tail keywords at scale, say, for your entire website, you would have to turn to a dedicated long tail keyword research tool.
Check out our latest video for beginner-friendly tips and tools.
What makes Rank Tracker a powerful long-tail keyword tool is that it has not one, but 9 different keyword research methods:
Download Rank TrackerYou can use some or all of them and end up with tens of thousands of keyword suggestions for your website. Let me walk you through the process.
Step 1. Launch Rank Tracker, enter the URL of your site, and click Finish to create a project. The tool will immediately identify a few of your main keywords and add them to the rank tracking dashboard.
Step 2. Switch to the Keyword Research tab and check for Ranking Keywords: enter your page URL, configure search method (you can search the whole domain or the exact URL) and settings (desktop or mobile, preferred search engines as well), and hit Search. In a while, the software will show hundreds of Google keywords the page is already ranking for.
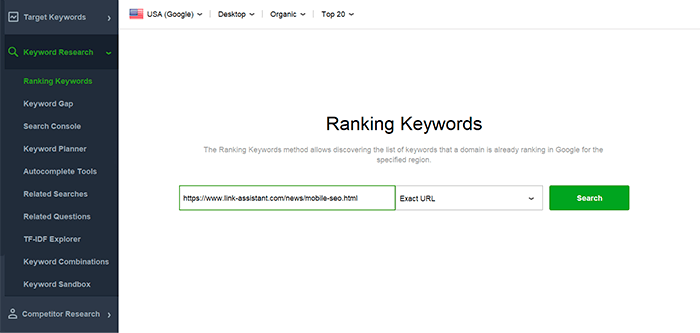
You can change the settings to research keywords coming from mobile devices. That can bring a strikingly different set of keywords. For example, the wide-spread use of smartphones changed the way mobile searchers formulate their queries: when deciding to buy some ordinary stuff, people started to look through reviews more, searching for the best alternatives, or whatever else should I choose.
Step 3. Let's try Google Autocomplete and Related Searches. These research methods draw on Google's recommendation system, the same one we discussed earlier. Except in this case no manual work is involved. All you have to do is enter a few of your seed keywords and the tool will do the rest:
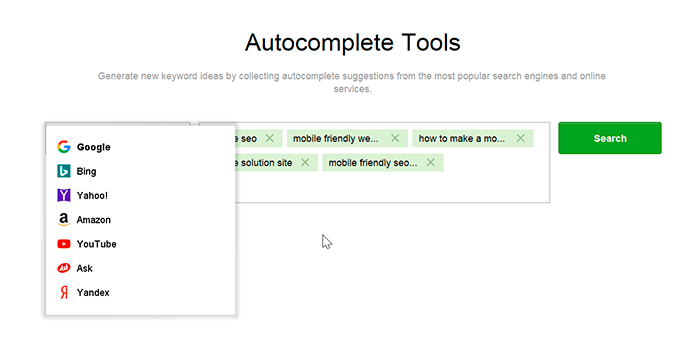
When it's done, you'll have up to several hundred new terms you could target.
Repeat this process for other autocomplete research methods, such as the Autocomplete tool for Bing, Amazon, YouTube — the researched keywords will be pretty different.
Step 4. Try the Related Questions method to discover question-like queries. These too come directly from Google's recommendation system, except the search for keywords is fully automated and can be done at scale. Just enter one or more of your seed keywords and the tool will collect commonly asked questions around the same topic:
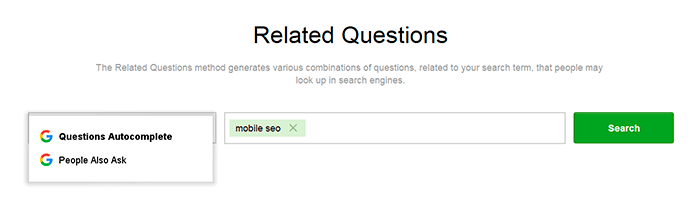
Step 5. Finally, switch to the TF-IDF Explorer. It allows finding topical long-tail keywords that your top-ranking competitors often use, but you might have missed. The keyword tool will provide a list of popular keyword phrases, their basic search stats, and how frequently your competitors use them:
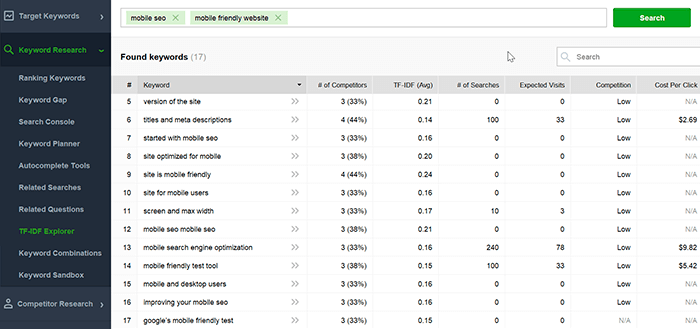
Step 6. Switch to the Keyword Sandbox. This tab is where we store all of the keyword ideas generated with the above research methods:
Download Rank TrackerFor example, I've run a quick search for keyword ideas around the topic of bikes and ended up with almost 14,000 keywords in my sandbox. Now, that is entirely too many and most of these keywords are not even long-tail. To narrow our selection of keywords down, let's move onto the second stage of keyword research — applying filters.
Another great thing about Rank Tracker is that it collects a bunch of metrics for each keyword discovered during the research stage. We now can use these metrics to evaluate our keywords and determine which ones are worth the effort.
For long-tail keywords, I prefer to apply three filters:
Filter 1. Keyword length. Set this filter to show keywords that are three words or longer. As discussed before, longer keywords are generally indicative of a smaller niche where it is easier to compete for rankings.
Filter 2. Keyword difficulty. Set this filter to show keywords with a difficulty score of less than 40. I'm using this setting as a rule of thumb, but you are free to select your own cut-off point. If you have a more authoritative website, you can choose to go against stronger competitors and vice versa.
Filter 3. Number of searches. Set this filter to show keywords with a search volume of above 250. Here too, you are free to select your own cut-off point. If your market is very small, then perhaps even 50 searches per month are a big deal.
Here is what the filters look like in Rank Tracker:
Download Rank TrackerTracking longtail traffic has already become harder since Search Console filters queries for privacy reasons… identifying longtail keywords… becomes impossible.
Once everything is set, click OK and the list of keyword ideas should become much shorter. In my case, once I've applied the filters I ended up with under 200 keywords, down from 14,000. Now my list is much more manageable:
Download Rank TrackerIf you are unhappy with the number or the quality of the remaining keyword ideas, then you can either change your filters or go back to the keyword research methods and look for more ideas using new seed keywords or different settings.
Another thing you can do is filter out negative keywords by vocabulary. For example, if you are selling premium merchandise, you are unlikely to want a customer who searches for cheap, popular, or free items, so just exclude these terms from your keywords. In the same way, you can exclude competitors' brand name searches, unnecessary locations, activities, or services that your website is not expected to cater for.
Now that you have your list of high-potential long-tail keywords, you can choose which ones are a good fit for your website. Simply scroll through the list and see if it makes sense to create a page on these topics.
At this stage, you can also easily group your keywords with the help of the Keyword Grouping feature.
Whenever you find terms that are a good long-tail fit for your website, select them and hit Move Selected Keywords To Rank Tracking.
These keywords will then appear in the Target Keywords module, where your Rank Tracking and Keyword Map dashboards are.
In Rank Tracking, you can once again do the keyword difficulty check. Switch to Keyword & Rankings tab and in the lower workspace select the Keyword Difficulty tab. There you will see pages ranking in the top 10 for the selected long-tail keyword, alongside other important stats, such as InLink Rank, Domain InLink Rank, and how many sites are linking to the page. Based on this, you can estimate how much effort it will take to rank for the keyword.
Download Rank TrackerIn the Keyword Map module, you can assign a keyword to a page (or several terms or the whole group at once): right-click on them and hit the Assign Keywords To Landing Page button.
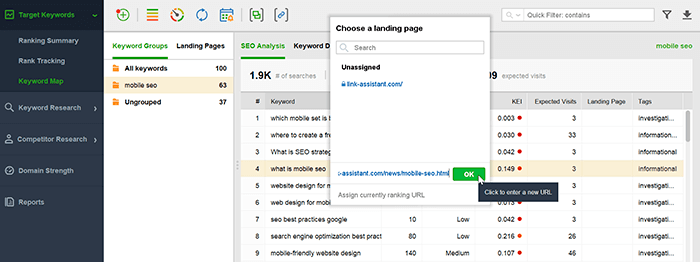
This way, you'll be able to easily see the distribution of long-tail keywords over each landing page in your keyword map. It will make optimizing the pages at the next step quicker and easier: keyword mapping will help you manage SEO copywriting, track ranks of the landing pages and fix issues, like traffic drops or keyword cannibalization.
By now, you should have a pretty extensive list of keywords mapped to each of your landing pages in Rank Tracker. It's time to work them into your content.
The easiest way to optimize your pages is with the WebSite Auditor tool — its Content Editor dashboard lets you edit your pages in live mode.
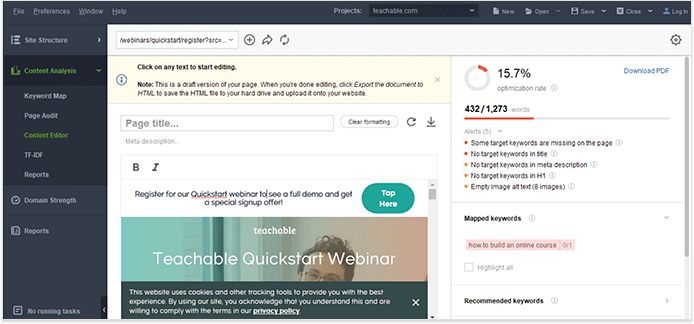
Paste the link to a page you want to optimize (or create a new one), add your main keyword, wait for a moment while the software conducts a page audit — and you have a list of tips on how to optimize your page. Use the tips to insert missing keywords throughout your copy.
As we've already discussed at the beginning of this article, long-tail keywords are a great fit for section headings of your pages. For example, let's say I run an online bike store and I have a blog post with the title How to choose a bike? Now, this type of guide is easy to split into several semi-independent sections, each of which can be dedicated to a different long-tail keyword. If I choose my keywords right, Google will be able to use my content to satisfy a whole range of search intents:
If you have a bunch of long-tail keywords that seem relevant to a page, but you can't work them in organically, then consider adding a FAQ section. Turn your list of keywords into questions, come up with answers, and add a section at the end of your page. It works great for product pages, landings, and all kinds of service pages (about, contacts, terms & conditions, etc.). The added benefit of FAQs is that you can enhance them with schema markup and improve your chances of being noticed by Google.
Internal links are great spots for your long-tail keywords. Put them in the anchor text when you insert a link to a page on another page, and make sure to keep the anchors diverse and natural-sounding. It is advised to link from pages ranking for long-tails to pages with broad, more popular keywords (for example, from product to category). This will help to build up the PageRank and make certain pages more prominent.
The same is true for the backlinks that you can control. Whenever you link to a page from an external resource (be it a guest post or another website of yours), use a variation of the long-tail keyword for the backlink's anchor text. External links have to be integrated into the content so that it would be difficult to remove them without rewriting the text. Long-tail keywords serve this purpose very well.
How long can keywords be?
Keywords can be as short as one word or as long as a full sentence. Long-tail keywords typically contain 3–7 words, but voice search queries can stretch to 10+ words.
How do I find longtail keywords?
You can find longtail keywords using Google Autocomplete, People Also Ask, related searches, or specialized tools like Rank Tracker, Keyword Tool.io, and Google Keyword Planner. These tools automate longtail keyword research and reveal phrases your competitors may miss.
How to use long tail keywords effectively?
Use long tail keywords in blog headings, product descriptions, meta tags, and FAQ sections. Build dedicated pages around them and link internally to broader pages for authority flow.
What’s the best long tail keyword generator?
Rank Tracker offers multiple research methods in one place, making it a powerful long tail keywords tool. Alternatives include Keyword Tool.io for autocomplete expansion and AnswerThePublic for question-based terms.
Are long-tail keywords still useful for PPC?
Yes. Targeting AdWords long tail keywords lowers cost per click, improves ad relevance, and drives more qualified leads compared to broad keyword bidding.
These are the basics for your long-tail keyword strategy to successfully target convertible traffic. To see how it works, you can also watch our webinar on long-tail keyword research. If you implement the long-tail keywords strategy properly on your pages, your site is guaranteed to increase visibility and expand to a larger, more convertible audience. Over to you.





