98022
•


Since 2002 updates, Google has made its major algorithm changes explicit. And when harsh penalties rolled out with the first Panda and Penguin updates, it became clear that the company was serious about creating an ethical environment for user search. Staying on top of the Google algorithm update history is crucial for webmasters, as SEO updates often bring significant SEO changes to rankings and traffic.
In fact, Google SEO updates take place every day and come mainly unnoticed. For instance, in 2021 Google made 5,150 improvements to search. Google confirms only major changes to its SEO algorithm – the updates that dramatically affect rankings. To help you make sense of these daily algorithm updates to Google’s search algorithm in the past years and major Google ranking factors, we've put up a cheat sheet with the most important updates and penalties rolled out in recent years, along with a list of hazards and prevention tips for each.
But before we start, let's have a quick check whether any given update has impacted your own site's traffic. SEO PowerSuite's Rank Tracker is a massive help in this; the tool will automatically match up dates of all major Google updates to your traffic and ranking graphs.
1) Launch Rank Tracker (if you don't have it installed, get SEO PowerSuite's free version here) and create a project for your site by entering its URL and specifying your target keywords.
2) Click the Update visits button in Rank Tracker's top menu, and enter your Google Analytics credentials to sync your account with the tool.
3) In the lower part of your Rank Tracker dashboard, switch to the Organic Traffic tab.
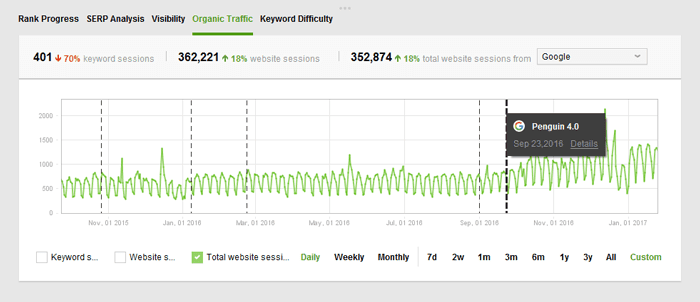
The dotted lines over your graph mark the dates of major Google algorithm updates. Examine the graph to see if any drops (or spikes!) in visits correlate with the updates. Hover your mouse over any of the lines to see what the update was.
Currently, the graph in Rank Tracker contains the dates of only major updates, namely Panda update, Pigeon update, Fred update, etc. But the graph is editable and allows adding those events that you deem relevant for your own tracking history. Simply right-click in the progress graph field and choose to add an event from the menu.
Did any of Google’s algorithm changes impact your organic traffic in any way? Read on to find out what each of the updates was about, what the main hazards are, and how you can keep your site safe. For convenience, the list starts with the latest algorithm updates.

After a relatively quiet span in terms of spam updates (since Dec 2024), Google rolled out the August 2025 Spam Update. This update was publicly announced and noted as the first major spam-focused algorithm update in about 8 months. As with previous spam updates, it applied globally and aimed at maintaining the quality of search results by weeding out spammy pages and tactics. Webmasters braced for impacts, as long intervals between spam updates can sometimes mean a more sweeping change when one finally comes.
By 2025, Google’s spam definitions are well fleshed out. The August 2025 update likely revisited known issues and perhaps addressed new emerging spam trends:
AI-generated spam content: With more content being produced by AI, some bad actors generate huge volumes of AI text stuffed with keywords, hoping to rank. Google’s SpamBrain surely evolved to catch AI spam that’s published without oversight. Sites doing this en masse could be severely hit.
Evasive link schemes: Spammers are always trying new link tactics – maybe 2025 saw an uptick in things like injecting links via widgets or PDF uploads for SEO. Google might have refined detection of unnatural link patterns. If your site’s backlink profile suddenly included a lot of links from dubious sources (perhaps a negative SEO attempt or an old link scheme coming to light), you might see ranking declines.
Cloaked malware pages: A perennial issue – some hacked sites show phishing or malware pages to users but hide from Google. The spam update likely continues to identify and demote any such compromised content. If your site’s security is lax and you got hacked without realizing, the spam update would treat those pages as spam and possibly impact your site’s overall rankings.
Stick to the rule: if it’s against Google’s spam policies, don’t do it. Some specific actions:
Audit new content for quality: If you ramped up content production with AI, review those pages. Make sure they provide value and aren’t just fluff around keywords. Remove or improve low-value pages. Also, ensure AI content hasn’t introduced hidden spam (sometimes AI can generate odd outputs or base content on spammy sources).
Check your backlinks regularly: Use SEO SpyGlass or Google Search Console’s link report to monitor new inbound links. If you see a surge of links from irrelevant or low-quality sites, disavow them preemptively rather than wait for Google to possibly trust them less (which could indirectly hurt you). While Google is good at ignoring bad links, a spam update might recalibrate values and suddenly those bad links drag you down until they’re disavowed.
Secure your site (again): 2025 websites should all be on HTTPS and regularly scanning for vulnerabilities. If you haven’t, consider a security plugin or service. Google’s August 2025 update reminds us that even a few spam pages on an otherwise legit site can tarnish it. Schedule periodic security audits.
Follow content guidelines: If you’re not sure whether something might be seen as spam, refer to Google’s Webmaster Guidelines (now part of Search Essentials). For example, doorway pages (multiple pages targeting similar keywords to funnel to one destination) are a no-no – if you still have any, consolidate them. The same goes for keyword stuffing: ensure your content reads naturally, not like a string of search terms.
With the August 2025 Spam Update, Google reinforces that integrity in content and SEO practices is non-negotiable. By adhering to that principle, you not only dodge penalties but also build a site that users trust and that can sustain high rankings regardless of algorithm changes.

Continuing the trend of 2–3 core updates per year, Google released the June 2025 Core Update at the start of summer. This update lasted a bit over two weeks. While Google didn’t provide unique insights about this specific update, it’s understood to be another general quality improvement. By mid-2025, Google’s core updates have become somewhat routine, each one building on the last to incrementally improve search results. The June 2025 Core Update likely included tweaks to how content is evaluated, possibly integrating better understanding of user intent and content relevancy.
If your site successfully navigated all the prior core updates, you probably fared fine here too. Potential hazards would be:
Content stagnation: Sites that haven’t been updated or expanded in a long time risk falling behind sites with fresher, more comprehensive content. Google’s algorithms may favor content that is both high-quality and up-to-date, especially in niches where information evolves (tech, health, finance, etc.). A static site could see slippage.
Competitive landscape changes: A core update is like a re-ranking based on current conditions. If new competitors or existing ones dramatically improved since March 2025, June 2025 might have reshuffled rankings to reflect that. Thus, your site could dip even if you didn’t do anything wrong, but rather others did things better.
Edge-case content: Sometimes core updates target specific patterns. For instance, perhaps Google got better at understanding when content is borderline spammy vs. genuinely informational in certain query types. If you have content that sits on the fence (e.g., “SEO bait” content that is mostly fluff around a keyword), that might lose positions to content that directly answers the query.
The playbook remains the same, with a few additions to consider:
Embrace the latest search features: By 2025, Google’s search results often include AI-generated overviews (as part of Google’s Search Generative Experience), rich snippets, and more. While the core update doesn’t directly tie to those, sites that structure their content well (using schema, clear headings, concise summaries) may be more likely to be featured. In optimizing for core updates, also optimize for featured snippets and AI overview inclusion – e.g., have a brief paragraph that clearly defines or answers the primary topic question. This can help you both rank well and possibly get picked up by AI summaries.
User engagement focus: If available, use tools like Google’s Search Console Insights or behavior analytics to see how users interact with your content. High bounce rates on important pages might indicate the content isn’t meeting user needs as well as it should. Improving those pages (or providing a more direct answer sooner on the page) can both improve engagement and make the page more helpful, aligning with what Google wants.
Leverage community feedback: By now, you might have a community or readership. Listen to their feedback. Comments, forum discussions, or social media can reveal if your content has gaps or errors. Proactively fixing these not only makes your audience happy but also tends to improve your SEO. A well-maintained page that addresses user concerns can perform better after core updates.
Keep building authority: 2025’s landscape values not just what you publish, but who you are. Continue to build your site’s authority through ethical link-building, PR, and perhaps author reputation. If you have experts, have them publish under their own name with a detailed bio (Google can recognize author entities). A strong positive reputation can indirectly influence how your site is perceived (for instance, a medical site with content by accredited doctors will likely have an edge).
Overall, the June 2025 Core Update likely rewarded ongoing SEO diligence. If you maintained your site well through 2024 into 2025, you were probably rewarded or stable. If not, use this update as the stimulus to reinvigorate your SEO strategy.

Google’s March 2025 Core Update was the first major algorithm update of 2025 and followed the pattern of a spring core update. It took about two weeks to complete. Google described it as a “typical core update where Google updates its core ranking system to make search results more relevant and helpful.” In many respects, it was a continuation of the core update philosophy from late 2024: rewarding genuinely useful, people-first content and demoting content created just to game rankings. This update was less eventful than March 2024’s huge update, but it still caused significant volatility in search rankings during the rollout.
The usual broad core update impacts were observed:
Sites with unresolved quality issues that might have survived previous updates by luck felt the sting. E.g., if your site still had a lot of thin pages or mediocre content, this core update might have been the tipping point for Google to demote those.
No major new targets were identified by Google publicly – it wasn’t like a new system introduction. But some SEOs reported that the March 2025 update didn’t seem as widespread in impact as some prior ones, suggesting it fine-tuned rankings rather than overhauled them. Thus, hazard mainly lies in how you compare to competitors. If a competitor improved significantly and you did not, you might have lost rankings even if your site didn’t “get worse.”
Stability for well-optimized sites: Many webmasters noted that if they had taken all the prior advice (improving content, etc.), March 2025 was relatively stable or even positive for them. So the hazard was primarily for those who hadn’t yet adapted fully to Google’s quality standards.
By this time, your SEO strategy should be deeply rooted in quality content and site excellence:
Conduct a fresh content audit: It’s 2025 – content that was great in 2019 might be outdated now. Update or prune content that no longer serves users. Merge pages if you have overlap, to create one stronger resource. Tools like WebSite Auditor can list pages with low word counts or outdated optimization. Don’t forget to update things like title tags and meta descriptions if the page content has changed (to maintain relevance).
Review Google’s core update guidance again: Google’s documentation on “What site owners should know about core updates” is evergreen. Re-read their questions. For instance, they emphasize that a drop doesn’t necessarily mean a violation or problem – sometimes other content is deemed more relevant. The remedy is often to make your content even better. Look at the pages that replaced yours in rankings – analyze what they have that you don’t, and consider adding similar value.
Enhance user experience signals: While Google officially says core updates aren’t about things like Core Web Vitals or mobile-friendliness (those are separate algorithms), a poor UX can indirectly hurt engagement and thus perceived quality. By 2025, most sites have implemented the basics. But if you haven’t (secure your site with HTTPS, ensure mobile responsiveness, improve site speed), you’re behind the curve. Use WebSite Auditor’s Page Audit or Google’s PageSpeed Insights to catch any lagging technical issues.
Be cautious of AI content: With the boom of AI, ensure you’re not publishing AI-written content without human oversight. Google’s stance is quality, not the method of creation, but many AI-written pieces can sound generic or have factual errors. Continuously fact-check and enrich any content that started with AI assistance. If March 2025 made one thing clear, it’s that “helpful, reliable, people-first content” remains the north star
If you were impacted by this update, use it as a learning opportunity. Often, sites that fall in one core update can bounce back in a future one if they put in the work – improving content, disavowing spammy links, enhancing site structure, etc. There’s no penalty to “fix” in core updates, only a higher bar to meet. Reach that bar, and you should see positive results in subsequent algorithm refreshes.

Right on the heels of two core updates, Google also launched a December 2024 Spam Update. This was a global spam algorithm update, similar in nature to the prior ones in March and June, but interestingly timed at the end of the year. Google said it was a broad update addressing spam in all languages. Many SEO commentators noted that this update hit particularly hard and fast, with some sites seeing impacts within just a couple of days of the announcement. It was described as more widespread than some previous spam updates, suggesting that it caught a lot of sites off guard – possibly because spammers ramp up activity during the holiday season, and Google responded accordingly.
The usual suspects for spam updates applied, with perhaps extra scrutiny:
Affiliate spam: Late in the year, spammy affiliate sites or coupon sites often proliferate. This update likely cracked down on those auto-generated “best deals” pages that provide little real value. If a site was churning out doorway pages for holiday sales or using scraped content to rank for Black Friday/Cyber Monday terms, it would be at high risk.
Cloaked content and link spam: Given its broad nature, any lingering cloaking schemes or link networks could have been taken down. By this time, SpamBrain was very advanced. If your site somehow benefited from a private blog network or paid links through 2024, this update might have neutralized those gains (or worse, penalized the site).
Hacked content injections: A spike in hacking and defacement can occur around holidays when webmasters are slower to respond. Google’s systems might have targeted hacked sites aggressively so that hacked pages (often filled with spam or malicious redirects) don’t rank. If your site was unknowingly hacked and showing spammy content, you’d likely see a sharp drop.
At this stage, your anti-spam regimen should be well-established:
Year-end audit: It’s wise to do a quick audit of your site at year-end. Look for any unusual new pages in Google’s index (site:[yourdomain]) that you didn’t create – a sign of hack. Check Google Search Console coverage and security reports. If anything looks off, fix it immediately (restore clean backups, remove injected code, etc.).
Reconfirm your link philosophy: If you engaged in any link buying during the year thinking it slipped under Google’s radar, assume it won’t slip past year-end. The December spam update was powerful; many reported significant ranking drops attributed to link issues. Use SEO SpyGlass’s Penalty Risk to identify links that might be causing trouble. It’s better to disavow a spammy link than to let Google possibly misattribute it to your SEO strategy.
User-first approach to affiliate content: If you run monetized content (like product roundups or coupon codes), make sure it’s truly useful. For instance, a coupon site should have only valid, updated coupons and maybe extra info like success rates or tips for saving – not pages of expired codes just for SEO. A product roundup should have genuine comparison criteria and perhaps personal testing notes, not just a rewritten manufacturer blurb for each product.
Stay secure and up-to-date: Keep your CMS, plugins, and libraries updated to prevent hacks. Use secure passwords and enable 2FA for critical accounts. Google can penalize you for spam even if you didn’t put it there (hacked spam), so prevention is key.
By the end of 2024, Google had launched three spam updates and four core updates in that year. Surviving all that is an achievement — it means your site is likely well-aligned with Google’s definition of quality. The December 2024 Spam Update was the final test of the year; passing it means you head into 2025 with a clean bill of health in Google’s eyes. Keep doing what you’re doing (provided it’s white-hat!), and always be ready to adapt as Google refines its algorithms.

In a surprise move, Google launched the December 2024 Core Update just one week after the November core update had finished rolling out. This was an unprecedented back-to-back pair of core updates. Google acknowledged the odd timing, explaining that different core systems are always being improved, implying that the December update addressed a separate set of ranking system tweaks that weren’t bundled into November’s. The rollout of the December update was swift (only six days), especially compared to the lengthy core updates earlier in the year.
The SEO community noted that this December core update was more volatile than the November update, though still not as drastic as March or August 2024. It caught many off guard due to the proximity of two core updates; some sites that had just adapted to November’s changes had to evaluate their standings again in mid-December.
Considering its quick succession:
Sites that saw gains in November might have seen partial reversals or further gains. Because November and December were likely targeting different aspects, it’s possible a site could uptrend in one and downtrend in the other. For example, maybe November rewarded your content quality, but December adjusted something about link signals which you were weaker in (or vice versa).
Sites that panicked or made hasty changes after November: If someone radically altered their site in the week between updates (not that there was much time), those changes might not have the intended effect, or could even hurt if they misdiagnosed the issue. It’s a reminder that knee-jerk reactions to one update can be risky.
Ecommerce and holiday sites: The timing right before the holidays meant e-commerce sites were concerned. If an online store dropped in rankings in mid-December, that’s painful. The hazard here might be if a site had thin product pages or auto-generated descriptions – core updates can affect those. Google historically doesn’t love doing big updates in late December, but this one was done by Dec 18, presumably to minimize Christmas week disruptions. Still, any site with weaknesses in content or technical SEO during the crucial season could have been impacted.
All core update wisdom applies, with emphasis on not overreacting:
Don’t double-count issues: If you were hit in November and again in December, carefully identify if it’s actually two separate things or just one prolonged issue. For instance, check if different sections of your site were affected in each update. November might have hit your blog content, while December might have hit product pages (or vice versa). Use analytics segmentation (by directory, by content type) to spot patterns.
Maintain course on quality: Google launching another update so soon reinforces that their direction didn’t change – they are simply fine-tuning. So, do not revert any quality improvements you made. Instead, look for additional enhancements. Perhaps the December update wants to see better internal linking or improved meta information (since it was so quick, some theorized it might relate to how sites interlink content or something less content-heavy).
Monitor external factors: It’s possible the December update also calibrated how sensitive the rankings are to factors like user engagement or backlink freshness. Keep an eye on your link profile – LinkAssistant can help discover new link opportunities to strengthen your site’s authority if you suspect you’re lacking there. Similarly, ensure your content remains fresh if appropriate (don’t let key pages become outdated).
Learn from competitors who consistently rank: By end of 2024, identify any competitor site that seems to weather all these updates well. Study their site: content depth, site architecture, new content frequency, etc. They are doing something right in Google’s eyes across multiple updates. Emulate the good (not by copying content, but by adopting successful strategies).
Google’s explanation for the rapid second update was basically “we have multiple things to improve, and they don’t always line up with our quarterly update schedule.” So, the takeaway is: always be ready. If your site is solid, an extra core update won’t knock you down. If it does, pick up the pieces by following the evergreen principle: make your site better in content, usability, and trust – and you’ll likely rebound.

The November 2024 Core Update was a more “standard” core update by Google’s description. Google stated the purpose was “to continue our work to improve the quality of search results by showing more content that people find genuinely useful and less content that feels like it was made just to perform well on Search.” In simpler terms, it’s the ongoing battle against SEO-first content in favor of user-first content – a theme we’ve seen with helpful content and core updates over the past couple of years. This update ran for 24 days. Interestingly, it was followed very quickly by another core update in December, which was an unusual cadence for Google (two core updates back-to-back).
Reports from the field suggested that the November 2024 Core Update was a bit less volatile overall than the earlier 2024 core updates (March and August). Many sites saw changes but not to extreme degrees.
The hazards here were typical for a core update:
Content that “feels made just to rank.” If your site had any remnants of content that exist solely for attracting search hits – maybe old clickbait articles, or pages targeting obsolete keywords with no real value – those would be prone to drop.
Sites resting on laurels: If you hadn’t updated your site or content in a long time, other sites that have been actively improving might have outranked you. Core updates often reassess comparative quality, so a competitor’s steady improvements can result in your relative decline.
On the positive side, websites that diligently focused on user satisfaction likely saw gains. If you saw users responding well to your content (e.g., more sharing, more direct traffic, better retention), that often correlates with core update improvements.
Continuity in best practices is key:
Review Google’s own statement: The quote above basically tells you what to do – make content that people find genuinely useful. It may help to occasionally step back and critique your site as if you were a user. Is there something more you’d want from an article? Are your pages answering all common questions on that topic? Using tools like Content Editor can reveal popular questions or subtopics (from People Also Ask boxes, etc.) that your content might be missing.
Holistic site quality: By this point, you should assume Google looks at site-wide signals too. The presence of some thin pages can be a drag on overall site quality perception. If you haven’t already, remove or improve any low-quality pages. Perhaps run a Website Auditor crawl for content quality – look at word count, duplicate content flags, and low PageRank (internally) pages. This can pinpoint sections of the site to either prune or polish.
Stay updated on guidelines: In late 2024, Google’s documentation and guidelines had seen updates (e.g., a refreshed Search Quality Rater Guidelines adding the “Experience” factor, turning E-A-T into E-E-A-T). Ensure your knowledge is current. For instance, the additional “Experience” criteria means first-hand experience content is valued. If your site can incorporate more real-life examples, case studies, or personal experience, do it.
Plan for resilience: Given another core update was coming a month later (unexpectedly), the lesson is to always be ready. Keep a habit of continuous improvement – core updates favor those who iterate and enhance their sites regularly, not just in reaction to ranking drops.
By following these practices, the November 2024 update should either treat you well or at worst be a small blip. The goal is that each core update finds your site a little better than before, so you’re moving in a positive direction or recovering ground steadily.

The August 2024 Core Update was another significant broad core algorithm change, and notably, Google indicated it took into account feedback from the previous year’s helpful content update (Sept 2023). Many small and independent publishers that had struggled after the Sept 2023 update saw some recovery with this August update, implying Google tweaked how harshly the Helpful Content system applied its criteria. The update ran for about 19 days and was characterized by SEO commentators as a “rather large core update” in terms of impact.
Besides the usual core update considerations, specific context for August 2024 includes:
Sites with genuinely useful content that were previously under-valued might have gained (which is a good thing), but conversely, sites that gained in Sept 2023 by perhaps removing tons of content or heavily altering their strategy might have seen some adjustments. In other words, if someone over-pruned content to recover from Sept 2023, August 2024 might have readjusted rankings once quality improved across the web.
Thin affiliate sites or AI-heavy sites that survived up to 2024 could have been hit here if they hadn’t been caught earlier. Every core update is another chance for Google to identify patterns of low-quality content.
No single niche was called out, but given the mention of small publishers, there’s a suggestion that some previous bias against certain smaller sites was corrected. If your site is smaller but high-quality, you may have gained; if your site is large but coasting on authority with mediocre content, you might have lost some ground.
By now, the pattern is clear – focus on the fundamentals:
Quality and balance: If you removed a lot of content due to earlier updates (to eliminate unhelpful pages), consider if you can add new, high-quality content to fill any gaps in your topical coverage. Google likes to see sites continue to be relevant and comprehensive in their field. A news site, for example, that cut down on thin articles should start publishing well-researched articles to regain “freshness” and depth.
User feedback and engagement: One form of “feedback” Google might indirectly use is how users interact with sites post-update. Monitor metrics like time on page, bounce rate, and scroll depth. If Google’s tweaking how it values content, better user engagement will be a positive signal that your content is truly helpful. Use Google Analytics or behavior analysis tools to find pages where engagement is low and improve them (maybe the content isn’t meeting expectations set by the title, etc.).
Stay the course with E-E-A-T: Continue showcasing your experience and expertise. If August 2024 rewarded some sites that were previously hit, it could be that Google got better at recognizing truly expert small sites versus fluffy content on big sites. So, if you’re a smaller site, don’t be discouraged – double down on demonstrating your niche expertise. If you’re a bigger site, don’t rely only on your domain authority; make sure every article is as expert and trustworthy as it can be.
Technical health check: It never hurts, with any core update, to ensure technical issues aren’t holding you back. Run a crawl with WebSite Auditor to catch broken links, orphan pages, slow load times, etc. While core updates are mainly about content, a technically healthy site ensures your great content can be found and appreciated by Google.
The August 2024 update, coming after the monumental March 2024 update, showed that Google is continuously fine-tuning. Many sites saw positive corrections. If you were among them, congratulate yourself and keep improving. If you weren’t, use this time before the next update to elevate your site’s content further.

In mid-2024, Google confirmed a new ranking system update specifically aimed at deepfake content. With the rise of AI-generated media (images, videos, audio), Google took steps to ensure that deceptive or harmful deepfakes do not rank prominently in search. While details were sparse, Google’s stated aim was to “surface high-quality, non-explicit content — like relevant news articles — when it’s available, instead of deepfakes.”. This suggests that if someone searches for something that could yield deepfake results (for example, a celebrity’s name alongside a term like “video” which might lead to deepfake videos), Google will try to show authentic sources or news debunking the fake, rather than the deepfake itself.
This update is less about traditional SEO spam and more about content authenticity:
Websites that host deepfake videos or images without clear context or disclaimers could be negatively impacted. For instance, a site that shares doctored videos as clickbait might find those pages unable to rank.
Content farms that pump out AI-edited media (e.g., altering images of public figures or generating bogus audio clips) for traffic could see a decline. Even if their SEO (titles, tags) was good, Google is explicitly trying to filter such content.
On the flip side, legitimate sites that expose or discuss deepfakes (like fact-checking websites) might get a boost. If your site deals with news or facts, not being mistaken for a deepfake source is crucial.
For most honest websites, this update won’t require changes, but consider the following:
Avoid misleading uses of AI content: If you use AI-generated images or voiceovers, always provide context. Don’t present them as real. Mark them clearly (e.g., “Illustration generated by AI”). For example, if you have a history blog and you create an AI-generated image of a historical figure for illustration, say so. Transparency can help both users and search algorithms trust your content.
Don’t engage in deepfake sensationalism: Some sites might be tempted to share trending deepfake videos or images for quick traffic (e.g., a fake video of a celebrity doing something shocking). This may have worked before, but now it’s risky. It’s better to either not share such content, or share it only in the context of debunking it, citing credible sources.
Monitor image/video SEO: Keep an eye on how your multimedia content is performing. If you notice drops in image search or video search traffic around August 2024, audit those files. Ensure you’re not accidentally getting flagged. For instance, an AI-generated stock image on your site might be fine, but if Google misidentifies it as a harmful deepfake, you might need to use a different image or add more descriptive alt text and surrounding text to clarify its nature.
Leverage authenticity signals: If you produce original videos, consider using techniques like watermarks, logos, or even embedding metadata that assert authenticity. Google hasn’t said it uses such signals, but anything that distinguishes your real content from potential fakes could be beneficial. In written content, linking to authoritative sources and being factual will help you be seen as a reliable result, even in queries that might be affected by deepfakes.
The deepfake update reflects Google’s broader commitment to fighting misinformation. By focusing on trustworthy, authentic content, your site will naturally align with what Google wants to promote. If your content has nothing to do with deepfakes, simply continue following best practices – this update will likely never negatively touch you, and it may even protect your content from being outranked by deceptive media.

The June 2024 Spam Update was another confirmed update aimed at tackling spam in search results. Google characterized this one as a “general and broad” spam update, meaning it wasn’t focusing on a single niche of spam (like links or content specifically) but rather improving the overall spam-fighting algorithm’s reach and accuracy. Notably, Google also clarified that this update did not introduce automation of the new “site reputation abuse” policy – that aspect was still handled via manual actions for the time being. The rollout was relatively quick (about a week) and it was the only major spam update between March 2024 and the end of 2024.
While broad, this update likely revisited known spam vectors with tweaks:
Websites with spammy user-generated content (UGC) could be hit. If your site has forums or comments that aren’t moderated, Google’s improved systems might more aggressively downrank those pages or sections. For example, a Q&A site filled with spam answers or a blog with comment spam might see impacts.
Cloaking and sneaky redirects continued to be a prime target. A general spam update often means Google found new ways spammers were cloaking content or redirecting users, and adjusted the algorithm. Sites inadvertently using outdated practices (like showing Google a keyword-stuffed page but redirecting users to a cleaner page) could be caught in the net.
Spam in different regions/languages: Google keeps extending its spam handling to be truly global. If some languages or countries had unique spam practices slipping through, June 2024 likely addressed more of those. For instance, if a certain link network was primarily affecting a non-English market, this update might have neutralized it.
By this point, your site should ideally already be in good shape from previous spam updates. Still, as a refresher:
Moderate user content: If you allow users to post on your site, invest in moderation tools or personnel. Remove spammy posts and links promptly. Consider using nofollow or ugc attributes on user-submitted links automatically, to avoid any association with spam links.
Review site sections separately: It’s possible to have parts of your site flagged as spam while others are fine (for example, a blog that’s great but a neglected forum that’s pure spam). Use Google Analytics or Search Console to segment performance by subfolder. If one section’s traffic drops in late June 2024, investigate that section for spam signals.
Keep technical SEO clean: Ensure there’s no cloaking on your site – serve the same content to Googlebot and users. Don’t hide text or links in your HTML (e.g., using white text on white background, or zero-size text). These tricks are old, but some sites still have remnants of them which could trigger spam flags.
Educate editors and contributors: Sometimes well-meaning content creators might add unnecessary keyword-stuffed paragraphs or scrape a definition from another site thinking it helps. Make sure everyone involved in your site’s content knows to produce original, valuable text and to avoid any form of plagiarism or keyword stuffing.
In essence, the June 2024 Spam Update was another step in Google’s ongoing effort to clean up search results. If you had survived previous spam updates by adhering to guidelines, you likely came through this one unharmed. Staying vigilant and proactive on site cleanliness and quality is the best strategy, as always.

Launched concurrently with the March 2024 Core Update, the March 2024 Spam Update was part of Google’s expanded effort to fight search spam. Google’s Search Quality team introduced new spam policies in early March 2024 and began enforcing them algorithmically with this update. Two notable spam tactics in focus were:
Scaled content abuse: Mass-producing content (via automation or cheap labor) with the primary intent to manipulate rankings, not help users.
Expired domain abuse: Purchasing expired domains with established authority and repurposing them solely to host low-quality content for SEO gain
While Google has long fought spam, this update signaled an evolution of SpamBrain to handle these specific scenarios. The rollout took about 14-15 days, finishing in mid-March.
Sites or SEOs engaging in these newly-defined spam behaviors were directly in the crosshairs:
If you built a network of sites or bulk pages with thin, keyword-stuffed content (perhaps using AI or spinning to scale up), Google can algorithmically identify this pattern as “search spam” now. Even if the content isn’t a classic virus or trojan, the mere fact that it’s produced in bulk for SEO can trigger penalties.
If you acquired an expired domain (maybe a once-legitimate site) and put unrelated or low-quality content on it to piggyback off its old backlinks, that domain likely lost its remaining value. Google made it clear that without the original site owner’s oversight, such third-party content on a previously authoritative domain is considered spam.
General spam tactics (cloaking, hidden text/links, etc.) continued to be enforced, so all prior hazards from spam updates remain (hacked content, link farms, etc.).
The guidance extends traditional anti-spam wisdom with new specifics:
Don’t pursue quantity over quality: Resist the temptation to create 100 micro-sites filled with mediocre content. One authoritative site is far better than many thin sites. If you manage multiple domains, ensure each has a unique purpose and valuable content. Quality control is key – even if content is written by AI or multiple authors, have an editorial process to maintain standards.
Be cautious with expired domains: There are legitimate uses for an expired domain (like redirecting it if it’s a close variant of your brand, or reviving a truly relevant site). But if you do use one, rebuild it with extremely high-quality content that serves the audience that domain was known for. Also, disclose changes (so users aren’t deceived). If your intent was solely to leverage its backlinks or authority without providing value, you’re better off not using the domain at all.
Continue general best practices: Use SEO SpyGlass regularly to spot any spammy backlinks (which might increase if spammers create scaled content linking to you – a negative SEO attempt). Monitor Google Search Console for manual action notices, since Google mentioned both automated and manual actions would be used for these spam types. If you get a warning about “spammy content” or “unnatural links,” address it immediately by removing or disavowing the problematic elements.
Educate your team or clients: If you’re an SEO agency or have content freelancers, ensure everyone knows about these updated spam definitions. Sometimes spam occurs not out of malice but ignorance (e.g., a well-meaning content team might start mass-producing AI articles thinking more is better). Make sure the focus stays on helpful content creation, not just volume.
Google’s moves here indicate a tightening of what’s acceptable. The search engine wants to reward genuinely useful websites and demote those trying to game the system at scale. By keeping your tactics white-hat and user-centric, you’ll not only avoid penalties but also build a stronger site that can endure future updates.

Google kicked off 2024 with a massive core update in March. In fact, Google later stated that the March 2024 Core Update was one of the largest core updates in its history, updating several parts of its ranking algorithm at once. This update was notable not just for its length (taking 45 days to fully roll out – significantly longer than usual), but also for the substantive changes under the hood:
Google incorporated its Helpful Content system more deeply into the core ranking process, and aimed to reduce low-quality or unoriginal content in search results by 40% (a goal which they later updated to 45% during the rollout).
Several spam-related policies were introduced alongside (and as part of) this update – Google launched new spam definitions for “scaled content” and “expired domains” abuse on the same day, and a parallel March 2024 Spam Update (covered next) rolled out together.
This update was so broad that it didn’t target one specific niche; it was a sweeping quality improvement across the board.
Because multiple systems were updated, the March 2024 Core Update cast a wide net. Hazards included:
Low-quality content of any kind: If your site had pages that were merely rehashing others or created just to target keywords, this update likely hurt them. Google explicitly said after this update that users would see significantly less unoriginal content in results.
AI-generated content that isn’t up to par: By early 2024, many webmasters were using AI tools to create content. Google’s stance was that AI content is fine if it’s helpful. This core update, with its helpful content integration, would downgrade AI or auto-generated content that failed to meet the quality of “leading websites” on the topic. Sites relying heavily on unsupervised AI content may have seen drops.
Sites affected by previous helpful content updates: Google indicated this update took into account feedback from the September 2023 helpful content update. Many small publishers hit hard in Sept 2023 saw some recovery in March 2024 – conversely, sites that didn’t improve after Sept’s hit might have been hit again or further in March.
Given its scope, a multifaceted approach is needed:
Double down on content originality: Ensure every piece of content on your site has a reason to exist. Can you say it’s unique, thorough, and genuinely useful compared to what's already out there? If not, consider merging it with other pages or improving it. Use Content Editor in Website Auditor to compare your content against top competitors – it will suggest missing topics and help gauge if your content is thin or over-optimized.
Embrace E-E-A-T fully: March 2024 reinforced that Google is seeking quality. Update your site to highlight author expertise (add author bios, credentials), user trust signals (HTTPS, privacy policies, customer service info for e-commerce, etc.), and real experience (case studies, original research, images of your work, etc.). The better you demonstrate E-E-A-T, the more likely Google’s core algorithms will favor you.
Watch out for spam indicators: With spam policy rollouts alongside, make sure you’re not inadvertently tripping spam filters. For example, if you bought an expired domain and repurposed it, Google now may algorithmically view that as spam if the content is low quality. Ensure any such domains are filled with great content and not just used for redirects or link-building schemes.
Be patient and monitor recovery: This update took a long time to roll out. If you made positive changes (like removing a bunch of duplicate pages or improving content) during the rollout, the effects might not be seen until it was complete. In some cases, you might need to wait for the next core update for a full recovery. Use Google Search Console and analytics to monitor gradual improvements in indexation and ranking.
Webmasters noted that after this update, many search results looked cleaner – with less clickbait and more authoritative pages rising up (especially in “Your Money or Your Life” niches like health and finance). Aligning your site with this trend by being honest, helpful, and authoritative is the best defense and offense for core updates like March 2024.

This update to Google’s reviews system started just after the November core update began, creating overlapping changes for sites with review content. In Google’s communication, they signaled a shift in policy: going forward, the reviews system would be improved continuously and they will no longer announce future reviews updates. In other words, this November 2023 Reviews Update was the last time Google would publicly confirm a reviews-specific algorithm change. The update itself ran for 29 days, and like previous ones, aimed to refine how Google evaluates the quality of reviews on websites.
Sites that did not heed the earlier reviews updates (from Feb and April 2023) were most at risk. By this point, Google’s standards for reviews were well-defined. Potential hazards:
Any remaining thin or template-like reviews on your site could cause trouble. For example, if an e-commerce site hosts user reviews, a pattern of very short, generic reviews might collectively hurt the site’s review content quality.
Websites built entirely on low-value reviews (like certain affiliate sites with just a collection of brief product summaries) may have seen further drops. Google’s ongoing improvements mean the bar was raised even higher for what counts as a “helpful review.”
Overlap with the core update means some sites might mistake core-related drops for review-related drops. But if your non-review pages held steady and only your review pages fell, that’s a sign you were hit by the Reviews Update specifically.
By now, sites should implement long-term quality measures for all review content:
Embed reviews in a broader content strategy: Standalone review pages are fine, but consider adding more value – e.g., comparisons (“Product A vs Product B”), top 10 lists with detailed analysis, or guides that incorporate your review findings. This creates richer content that can perform well even without standalone “review” labels.
Encourage substantive user reviews (if applicable): If your platform allows user-generated reviews (like a forum or product comments), encourage users to leave detailed feedback. You might prompt them with questions (Was the product as described? What did you use it for? etc.). High-quality user reviews can augment your content’s value in Google’s eyes.
Use structured data appropriately: While not a direct ranking factor, adding proper Review Schema markup for your reviews can enhance how Google displays them (and ensure Google understands which parts of your page are reviews). Just avoid any schema abuse (like marking up fake reviews), as that could incur a manual penalty.
Finally, since Google won’t announce future “reviews updates,” it’s wise to continuously monitor the performance of your review pages. Any time you notice a gradual decline, it could be the reviews system adjusting. Keep improving your reviews and adding fresh, insightful ones to maintain your site’s authority in the eyes of Google’s ever-learning algorithm.

In an unusual sequence, Google rolled out yet another broad core update in November 2023, overlapping slightly with the tail of the October core update. Google mentioned that this November update involved “an improvement to a different core system” than the October update. This suggests that Google may have been tweaking separate aspects of its ranking algorithms in quick succession. The rollout lasted nearly four weeks, and it also overlapped with a November Reviews Update which started on Nov 8. Data from rank trackers indicated that the November 2023 Core Update caused even greater ranking volatility than the October update.
Similar to other core updates, content relevance and quality were key. Given Google’s hint that a different system was updated, some SEOs speculated that this might have touched things like the link analysis system or semantic understanding differently than before. While specifics are unknown, potential hazards include:
Sites on the edge of Google’s quality thresholds: A site that barely survived the October update might have been pushed down in November if another ranking factor (like backlink trust or semantic relevance) was recalibrated.
Sites with poor internal diversity: Some reports noted that this update aimed to ensure more diverse results. If your site had multiple pages ranking for many of the same queries (especially if they were of middling quality), Google might choose only the strongest and drop the rest, favoring diversity in search results.
Overlap with the Reviews Update (Nov 2023) means if you had a lot of review content, you needed to meet both core and review criteria (high quality, plus depth in reviews).
Many of the core update recommendations remain consistent:
Improve content depth and uniqueness: Strive to make each page on your site the single best resource for its topic. If Google is refining different parts of its system (like understanding synonyms, intent, or link signals), it’s doubling down on rewarding truly stand-out content. Enrich your pages with unique insights, up-to-date information, and multimedia where appropriate.
Monitor your backlinks and brand signals: Since this could involve another “core system,” ensure your off-page SEO is solid. Disavow any spammy links (in case Google’s link valuation changed) and build your brand reputation (mentions on authoritative sites, good PR, etc.). A strong, trusted backlink profile can help signal your site’s authority in the niche.
Patience and analysis: Because the rollout was long (nearly a month), you might have seen rankings bob up and down. Don’t react impulsively to mid-rollout fluctuations. Instead, once it’s done, use Rank Tracker’s SERP Analysis to see how your rankings settled vs. competitors. If certain competitors consistently outrank you post-update, study what they do well – page experience, content length, use of schema, etc. – and consider adopting similar best practices.
Ultimately, the November 2023 Core Update reinforced the trend that Google core updates in 2023 came frequently and demanded continual quality improvements. Sites that invest in SEO fundamentals and comprehensive content are typically the ones that weather these updates best.

Google surprised the SEO world by releasing another core update just a couple of months after the August update. The October 2023 Core Update rolled out almost simultaneously with the spam update (one day apart). Google again did not provide specific details about this update’s focus, calling it a standard core algorithm change. However, the overlap of a core update with an active spam update led to a lot of ranking volatility during October. Webmasters found it challenging to discern whether changes were due to core or spam factors. Additionally, a bug affected Google Discover traffic around this time, which Google later corrected, adding to the confusion.
All websites were subject to the core update’s effects. Given the concurrent spam update:
Some sites might have experienced compounded effects (e.g., a slight core-related drop made worse by a spam-related drop). If a site saw a big hit in early October, it could be suffering from both: overall content relevance issues (core) and some spam signal (spam update).
The core update itself, in isolation, appeared to be a standard broad update. Sites that noticed ranking declines without any spam issues likely had content that was outperformed by competitors after Google’s re-ranking. This could include pages that lacked comprehensive coverage of a topic, had poorer user engagement, or didn’t match the user intent as well as others.
Sites that saw gains were often those that had been investing in content quality and freshness, suggesting the October core update rewarded those improvements, even as it penalized others.
Treat this core update like any other, but also cross-check if the spam update might have been a factor:
Assess content quality anew: If you experienced a drop, perform a competitor analysis. Who replaced you in the rankings and why? Tools like Rank Tracker can help identify which pages gained while yours lost. Compare your content side-by-side with the new top performers. Is your article missing key subtopics? Is the format less user-friendly? Update your content to close those gaps.
Check for spam flags: Since a spam update was simultaneous, review your site for any spammy elements (as noted above for the spam update). It’s possible a site could recover from the core update part but still languish due to a spam issue, or vice versa.
Wait for stabilization: Because two updates overlapped, Google’s advice was essentially to wait until both rollouts finished before making major changes. If by late October you saw no rebound, then proceed with improvements. Always document your changes and monitor their effect on rankings over subsequent weeks and months.
Staying safe from core updates always comes back to quality. Continue creating original, useful content, and keep your site technically sound. That way, even if the timing of updates is unpredictable (like two in two months), your site will generally trend upwards over time.

The October 2023 Spam Update was a broad update aimed at fighting spam in search results. Google noted that this update improved its coverage in many languages and against various spam types. In other words, the spam-fighting algorithms (many powered by SpamBrain, Google’s AI-based spam detector) became more effective globally. The rollout coincided with the October 2023 Core Update (they overlapped), which made it a hectic period for SEOs as both spam and core systems were in flux.
Any site violating Google’s spam policies could be impacted. Specific spam tactics that this update targeted include:
Cloaking and hacked content: Sites that show different content to Google than to users, or that have been compromised to inject spammy pages/links, are a major focus. Google said this update improved handling of cloaking, hacked content, and scraped/auto-generated content.
Link spam and unnatural links: Although this was not a dedicated “Link Spam Update,” sites with egregious link schemes (buying or selling links, PBN participation) often see drops during spam updates. Google continues to nullify credit from unnatural links as it did in December 2022, so manipulative link profiles remain a hazard.
Spam in multiple languages: If your site has multilingual content, ensure all versions meet guidelines. Google’s improved language coverage means non-English web spam is now caught more reliably. For example, techniques that might have “slipped through” in languages like Turkish, Vietnamese, or Hindi are now under the spam algorithm’s lens.
The advice is consistent with prior spam updates:
Audit your backlink profile: Use SEO SpyGlass to check for toxic backlinks to your site. Remove or disavow links that are clearly manipulative or from spammy domains. The tool’s Penalty Risk metric can highlight links that might be devalued or harmful.
Avoid black-hat tactics: If you have engaged in any link schemes, cloaking, doorway pages, or scraped content, cease immediately and clean up where possible. For instance, remove auto-generated pages or spun content. Adhere strictly to Google’s Webmaster Guidelines for quality.
Improve site security: Since hacked content is a target, secure your site. Keep your CMS and plugins updated, and monitor Google Search Console for any security alerts or sudden appearance of unfamiliar pages. Promptly fix any hacking issues to minimize damage.
Leverage LinkAssistant for safe link-building: Instead of buying links, use LinkAssistant (part of SEO PowerSuite) to find legitimate link opportunities. It can help you organize outreach for guest posts or resource page links, focusing on white-hat link-building techniques that provide real value. By sticking to earned links and quality partnerships, you’ll avoid penalties during spam updates.
In summary, double down on ethical SEO. The October 2023 Spam Update is one more reminder that attempting to shortcut rankings with spam will backfire, and that Google’s anti-spam AI is constantly improving.

A year after the original Helpful Content Update, Google released a significant update to its Helpful Content system. Google described this September 2023 update as featuring an “improved classifier” for detecting unhelpful content. In essence, Google got better at identifying content that is made primarily for search rankings (rather than to help users) and at demoting such content across search results. This update also came with some updates to Google’s public Search Central documentation, hinting at what changed – for example, clarifying how the system treats **third-party hosted content, content that simply changes dates without adding value, and content added/removed to manipulate rankings.
Websites at risk from this update were those still employing search-engine-first content strategies. Specific hazards included:
Sites with lots of aggregated or AI-generated content that wasn’t genuinely helpful. The improved classifier could more effectively catch content farms or sites pumping out articles just to rank.
“Parasite” content on otherwise reputable sites: Google indicated that hosting large amounts of content from others (e.g., guest posts or sponsored content) purely for SEO gain could be considered spammy. This means even high-authority sites could be dinged if they opened their doors to low-quality third-party content.
Misleading freshness: Some sites attempt to game rankings by frequently updating the date on articles without substantially improving the content. The documentation updates suggested Google is aware of this tactic. Such manipulative date changes or content swaps can now be recognized by the helpful content system.
All the guidance from the initial Helpful Content Update still applies – create content for people first, not for search engines. In light of the improved classifier, you should:
Audit your content for true value: Comb through your site and identify pages that might be “fluff.” Ask the hard questions Google provided – e.g., “Does this page answer a question that actually has no answer?” or “Is this content mostly a rehash of what others have said?” If yes, either improve it significantly or consider removing it. It’s better to have a smaller site with truly helpful, original content than a large site full of filler.
Be transparent and authentic: If you accept guest posts or user-generated content, vet them for quality. Ensure any content on your site meets your standards and serves your audience. Also, avoid mass-produced content (even if using AI) unless you thoroughly edit and add originality to it. Google explicitly took a stance against content produced at scale for SEO purposes in its spam policies around this time.
Leverage Website Auditor’s Content Editor: The Content Editor can help you optimize content while keeping it human-friendly. It analyzes top-ranking pages and can suggest if your content is straying into “search-engine-only” territory (for instance, by flagging keyword stuffing or lack of depth). Use these suggestions to rewrite any pages that might be borderline unhelpful.
Recovering from a Helpful Content penalty can take time – Google mentioned it might require several months for a site to recover after removing unhelpful content. So, it’s best to be proactive: continually improve or cull low-value content. Over time, this builds a stronger foundation that future-proofs your site against helpful content system updates.

The August 2023 Core Update was one of Google’s major broad core updates in 2023. As usual, Google provided no specific new guidance or details about what it changed. Many in the SEO community noted that this update, while significant, felt somewhat muted compared to previous updates. There was definitely ranking volatility – lasting over two weeks – but it wasn’t as drastic a shake-up as, say, the core updates of 2021 or the one in March 2023. Sites across various niches experienced changes, though no single industry stood out as particularly hit or boosted.
All types of sites could be affected. Some patterns observed included:
Sites with outdated or stale content lost some ground to fresher, more relevant pages. This suggests Google may have placed more emphasis on content freshness and ongoing usefulness.
Websites that had previously “coasted” on old authority but hadn’t updated in a long time might have seen declines (anecdotally reported by some webmasters).
As always, pages with persistent quality issues (poor mobile experience, slow loading, lots of thin pages) were at risk.
Continue to follow core update best practices:
Keep content up-to-date: Review your top content periodically and update it if necessary. August 2023’s relatively mild impact on regularly updated sites suggests that freshness and relevance are important.
Use Google’s Quality Rater Guidelines as a compass: While these guidelines don’t directly determine rankings, they reveal what Google values. Ensure your site demonstrates experience, expertise, authority, and trustworthiness in its topic area. This might involve citing trustworthy sources, having detailed “About” pages, and getting credible backlinks.
Monitor your site’s metrics: Use Rank Tracker to watch for any traffic or ranking drops around the update dates. The tool can overlay update dates on your performance graphs, helping you see if the August 2023 Update correlates with a change in your SEO metrics. If you spot a correlation, prioritize that area for improvement (content quality, link profile, etc.).
In short, if you were unaffected or saw gains during this core update, it’s a sign you’re on the right track with your SEO. If you lost rankings, treat it as a prompt to audit your site’s content quality and technical health.

In April 2023, Google overhauled its Product Reviews Update into a more expansive Reviews Update. This change meant that Google’s algorithmic focus on review content now applied not just to product reviews, but to all types of reviews – including services, media (e.g. movies, games), destinations, and more. Google even updated its official guidance language: where it once talked about “product reviews,” it began referring simply to “reviews.” This April 2023 Reviews Update was relatively volatile, indicating a significant shake-up in search rankings for sites with review content
Sites that hosted low-quality reviews of any kind risked losing rankings. For example:
Thin affiliate websites with generic service reviews or travel destination “reviews” that were not based on real experience could be hit.
Websites that previously weren’t affected (because they didn’t have product reviews) but had other review content (like movie review blogs or local business review roundups) might have seen impacts if those reviews lacked substance.
Spammy or AI-generated reviews became more dangerous to use, as Google’s system now evaluates all review content similarly to product reviews.
The best practices for writing high-quality reviews are now universally applicable:
Maintain authenticity and depth: Whether reviewing a product, a service, or a piece of media, ensure the content reflects personal expertise and genuine analysis. For instance, a software review should include your hands-on experience, pros/cons, comparisons to competitors, and who it’s best suited for.
Follow Google’s review guidelines: Google’s 15-point checklist for reviews (originally for products) is now relevant to all reviews. Questions like “Did I provide evidence such as visuals or metrics to substantiate my conclusions?” or “Did I discuss comparable options?” are important for any review content.
Edit or remove shallow reviews: Audit your site for any reviews that don’t meet these standards. It’s better to improve them or remove them if they provide little value. For example, a 100-word movie “review” that just says “It’s great, I liked it” won’t cut it post-update.
By elevating the quality of all review content on your site, you’ll align with Google’s reviews system criteria and likely see improvements. Remember, after this update, Google indicated it will no longer announce future reviews updates – the reviews system will evolve continuously. This means you should consistently keep your review content high-quality, rather than waiting for sporadic updates.

This was the first broad Google core algorithm update of 2023. Google did not provide any new guidance specific to the March 2023 Core Update – it was another general improvement to search rankings. However, SEO tracking tools and experts observed that this update caused significant turbulence in search results. In fact, its ranking volatility was equal to or even greater than some prior core updates, indicating many sites experienced notable shifts (either upward or downward) during the rollout.
All websites are potentially impacted by a core update. Sites that had unresolved quality issues – such as duplicate or thin content, slow page speeds, or intrusive ads – were especially vulnerable. Given the high volatility, even sites that previously escaped unharmed might have seen changes. No specific “type” of content was targeted, but any weaknesses in content quality or site user experience could result in ranking declines under Google’s refined evaluation.
The guidance is the same as for any core update: focus on quality content and a good user experience. Perform a thorough content audit with WebSite Auditor:
Identify pages with thin content or high bounce rates and improve them by adding depth, useful information, or multimedia.
Ensure your site is technically sound – fix slow-loading pages, mobile usability issues, or any Core Web Vitals problems.
Consider the search intent your content serves. After core updates, pages that best satisfy user intent tend to rise. Update your content to better answer the queries it targets (monitoring People Also Ask and related searches for hints).
Also, revisit Google’s core update questions (e.g., “Does your content provide substantial value compared to other pages in search results?”). If you find gaps, work on those areas. There’s no quick fix for a core update hit – improvements may take until the next core update to reflect. But consistently refining your site’s content and SEO according to Google’s guidelines will pay off in the long run.

Google’s first algorithm update of 2023 was a refresh of the Product Reviews Update. Unlike previous iterations which only affected English, this update expanded Google’s product reviews system to support 10 additional languages. It was the last update specific to “product reviews” before Google broadened the concept to all types of reviews. The rollout lasted two weeks, and trackers noted this update was more volatile than earlier product reviews updates, suggesting significant ranking changes for sites with review content.
Low-quality or thin product reviews were the primary target. Websites that had been publishing short, unoriginal reviews (or reviews auto-generated without genuine insight) saw drops in visibility. Because the update now applied to other languages, sites with translated or non-English reviews also faced scrutiny. If a site had relied on superficial content (e.g., just rephrasing manufacturer descriptions or aggregating user ratings without added value), this update likely hurt its rankings.
Google’s best practices for reviews remained key. To avoid losing rankings:
Provide in-depth, authentic reviews: Ensure your reviews contain original research, pros and cons, comparisons, and evidence of hands-on testing or expertise. If you run a multilingual site, apply the same quality standards across all languages.
Add supporting details: Include photos, videos, or audio of the product in use, and links to multiple sellers where appropriate (Google explicitly recommends this). This demonstrates that your content is created to help users, not just to rank.
Use expert knowledge: Reviews written by enthusiasts or experts carry more weight. Make sure the author’s expertise is clear to both users and search engines (for instance, through author profiles).
By following these guidelines, you produce reviews that meet Google’s criteria and are less likely to be impacted by updates to the reviews system. (Note: After 2023, Google’s “product reviews” updates evolved into a more general “reviews system,” covered in the next update.)

This was the second broad core algorithm update of 2022, coming just after the Helpful Content Update had finished rolling out. Google provided no specific new guidance for this update – as a typical Google core update, it was a general refinement of Google’s ranking systems. Notably, industry observers reported that the September 2022 Core Update was less significant than previous core updates in terms of impact. Some sites saw ranking changes, but overall volatility was moderate compared to earlier core updates.
As with any core update, all types of content could be affected. Sites with thin or low-quality content and those relying on outdated SEO tactics were at risk of losing rankings. There were reports of mixed outcomes – some sites (e.g. reference and niche informational sites) saw improvements, while others (including certain news sites) experienced declines, even before the rollout was complete.
There were no specific fixes targeting this update. Google’s advice remained the same: focus on producing high-quality, people-first content and ensure your site follows Google’s core update guidelines. Review Google’s questions for self-assessing your content quality (e.g., is it original, authoritative, and does it provide real value to users?). If your site was hit by this update, take it as an opportunity to audit your content for quality. Use the WebSite Auditor to identify pages with thin content or poor user experience, and improve them. Strengthening your site’s E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) signals – for example, updating author bios, citing trustworthy sources, and improving site security – can help build resilience against core updates.

Soon after the Helpful Content Update, Google proceeded with a spam update which was pretty swift, from October 19 to 21, 2022. According to Google, they have their antispam systems working ongoingly and improve them sometime, announcing major changes. The link spam update was announced globally in all languages and targeted both ends that bought or sold links. It is the first time that Google started using its AI-based spam detection system titled SpamBrain.
Google representative John Mueller several times mentioned it in Twitter comments that mostly it was not necessary to disavow spammy links because their systems were able to distinguish and nullify them. In the SpamBrain update, the link credit that was previously generated due to purchased links was expected to get lost. Thus, the update was aimed to hit mainly websites involved in link purchasing.
As we covered many times before with the previous spam updates, the best thing site owners can do is avoid spammy linking tactics. If a site still got hurt by spam updates, one should put effort into cleaning up link profiles from spam and invest more in building quality backlinks. And you can use the SEO SpyGlass Backlink Checker to see how bad your backlinks are.
The tool takes into account all negative signals that may imply that links were built on a PBN or link directories, such as: too many outgoing links from the same page, IP, or C-class block; keyword stuffing in anchors, etc.
The tool shows a Penalty score which signals how likely this or that link can be penalized by Google. If you find too many links that were built from buying or selling and you can't get rid of them, then you can use the disavow tool to tell Google to just ignore them.
Download SEO SpyGlass
On the other hand, you can use the backlink checker to find good domains and gain high-quality backlinks naturally. Find out more about quality link-building in the post from a practicing SEO Ann Smarty.

This update introduced a new site-wide ranking signal based on machine learning. Google systems have been set to automatically identify content that seems to have little value, low-added value, or is otherwise not helpful to searchers. The first iteration targeted English pages. Next, the Helpful Content Update was expanded globally in all languages in the successive rollout on December 5, 2022 and two weeks onwards.
The update targeted content created with the sole purpose of ranking and is considered thus to be for search engines first. Instead, Google suggests creating people-first content. The update was aimed to downrank sites with a lot of unhelpful content. The algorithm was to be applied further automatically all the time, not as a temporary penalty. If a site had some good content that exposed evidence of being helpful for searchers, the pages with that helpful content still could rank well.
Google provided a short checklist with questions to help website editors to improve the quality of their content:
Google also stated that if a site lost rankings due to the Helpful Content Update, it would take several months to restore them. Google suggests deleting unhelpful content, yet, instead of just deleting pages, you can reverse-engineer the SERPs and update your content by creating well-written posts or landing pages for people. And you can use Content Editor in Website Auditor to create a neat copy that will be SEO-optimized and written for humans at the same time.
Download WebSite Auditor
Content Editor analyzes the top 10 ranking pages on the SERP for your keyword and observes that:
You can edit your texts on the fly in-app or just download the recommendations as a task to work with in other content writing tools.
Keep in mind that in the meantime, Google updated its Search Quality Raters Guidelines in several iterations, which does not have a direct link to rankings, but helps to understand how Google sees quality content. The document was updated in several steps, with the latest taken in December: Google added Experience as a necessary criteria to be considered within a site's E-A-T profile, which have become now E-E-A-T. So, another important step is to work on the authority of your website and provide more information regarding to its relevance and competences in your niche.
Here, Google keeps their own chronology of all ranking and core updates.

On June 3, Google reported about an algorithmic adjustment concerning title links. If the search engine finds a mismatch between the language of the title and the main content on the page, it may generate a title link that matches better the primary content.
Google suggests sticking to the best practices of implementing title links. Note that you can review all your existing title tags, title lengths, as well as multiple title tags in WebSite Auditor's Site Structure > All pages section.

The May 2022 Core Update affected all types of content in all languages, but particularly hit websites with autogenerated or thin content.
May 22 Core Update is said to have been one of the largest since 2021 and affected websites in all locations and languages. SEO experts noticed that the update hit hard on sites with autogenerated and thin content that had lost around 80-90 per cent of their traffic.
Another type of websites affected by this core update were sites having redirects. In the first week of the update, they even saw a positive ranking, but then strated to lose their traffic.
Another effect from this update was noticed on smaller websites with good internal linking: if they did not have that much authority as to be in top positions, they benefitted a bit after the update if they had done proper contextual internal linking.
An interesting impact of the May 2022 Core Update was a clean-up in knowledge panels and featured snippets. It looks like it's going to be harder and harder to get into featured snippets. Is there a way out? Improve yor website's EAT signals. As Google reiterates its mission to "make search results more helpful and useful for anyone", there is nothing else left to do as to abide by Webmaster guidelines and build up the authority of your websites.
In regards to May 2022 update, we suggest using WebSite Auditor to examine and improve your content.
1. Run the tool to audit your site and find pages with thin content. Go to Site Structure > Pages, switch to the On-page tab and sort the pages by Word Count column.
Download WebSite Auditor
2. In the lower workspace, you can examine lists of all internal and external links page by page. Besides, in Page Audit you can examine the existing content on each page. Among all, review the list of anchors in Content Audit > Body > Keywords in Anchors.
3. Besides, you can use the Visualization tool to review the internal linking of your website.
Next, use WA's Content Editor to create content for your pages. The tool suggests topic ideas and top keywords to use, based on the analysis of top competitors from the SERP.

On March 22, 2022 Google announced the third version of the Product Reviews update, the full rollout took about three weeks, completed on around April 11. The update did not make as much impact as it was the case with the previous December product reviews update and its first phase a year ago.

On February 28, Google started rolling out the Google Page Experience update for desktops. The rollout was announced to stretch over a couple of weeks, to be completed by the end of March, but then the company reported, the rollout was concluded on March 6.
This update built on top of the page experience update Google rolled out for mobiles between June and August 2021. This ranking launch is based on the same page experience signals as for mobile devices. It covers the Core Web Vitals metrics: LCP, FID, and CLS, and their associated thresholds now apply for desktop ranking. Other aspects of page experience signals, such as HTTPS protocol and absence of intrusive interstitials, remain crucial as well. Meanwhile, the mobile-friendliness signal is not applicable on desktop URLs.
The page experience update may have impacted rankings on desktops. Meanwhile, the page experience score may be not the only factor that impacts your rankings.
There are three metrics to keep in mind:
To understand how desktop pages are performing in terms of page experience, webmasters can use the Search Console report. The Page Experience report now includes two separate dashboards. The report shows the percentage of good URLs and the number of their total impressions. The numbers are approximate, since different factors are measured within different time frames. It also links to the section with Core Web Vitals warnings and errors, indicating the number of URLs that need fixes.
You can use WebSite Auditor as well to detect pages speed issues for both desktop and mobile devices. Let WebSite Auditor scan your site and find technical SEO issues regarding page speed and mobile friendliness. Alternatively, you can grant access to the PageSpeed API and get all the data straight from Google. You will have all URLs with critical issues (for each issue individually) listed in the Site Audit report.
Also, you can check page speed for each separate URL in the Page Audit > Technical Audit report. There you will see the page speed score and the list of the diagnozed issues, which you can copy/export and send to your developers for fixes.
Download WebSite Auditor

The update concerns companies with a physical location who need visibility in Google Maps and the local pack.
On December 16, Google reported concluding a local search update which started to roll out on November 30 and ran through December 8. The local search update has been nicknamed the Vicinity Update for the impact it has made on Google Maps results: now the local search results are shown based on the listing's proximity to the searcher query. The update involved a rebalancing of various factors they consider in generating local search results. Google referred to the general guidance for businesses to improve their local search presence, according to which results are rankied according to three main criteria:
To meet the requirements, make sure you've fulfilled the following recommendations:
For more information, check out our guide to Local SEO Ranking Factors in 2021.

On December 1, 2021, Google reported rolling out another major update since April related to product reviews in English. The rollout is promised to take place within three weeks and may impact the way product reviews rank in search engines.
The update creates concerns for sites with numerous low-quality thin-content reviews.
Google suggests sticking to the best practices and writing high-quality content that proves the authenticity of the reviews. In addition to the guidelines on writing reviews that were published in April, there are a couple more tips:
Add supporting visuals, audio, or other links that prove the reviewer's experience in using the product;

Google announced a broad core update to roll out from November 17 and two weeks onward. The SEO community was a bit stunned by meeting a core update just on the eve of Thanksgiving and Black Friday. Probably, stakes were not that high because experts had noticed SERP volatility in favor of some big retailers. Meanwhile, this core update gave a boost to reference materials like dictionaries, Wikipedia, some popular directories, law and government resources. However, there was a decline in the visibility of news websites. A noticeable shakedown was registered for the health category. Take notice that these are the stats measured while the update was still rolling out. Google kept pretty laconic about this update, referencing as usual to its guidelines for webmasters.

Launched: November 3, 2021
Rollouts: Until November 11
Goal: Hit spam content
Since June 2021, Google has implemented a series of counter-spam updates. The first in the series was Google's response to New York Times articles documenting how the slander industry preys on victims of online slander. Google has even created a new concept it called “known victims.” According to NYT, the search giant was changing its algorithm to prevent slanderous websites from appearing in the list of results when someone searches for a person’s name. This has been a part of a major shift in how Google demotes harmful content.
This November, Google confirmed another spam update which started on November 3 and rolled out within a week. According to Google,
Spam updates deal with content that doesn't follow our guidelines. Core updates are simply an adjustment to how we assess content overall.
This update has made a more tangible impact on SERPs, presumably targeting cloaked content injected with links.
Cloaking is a black-hat SEO technique in which content presented to the search engine spider is different from the visible content presented to the user's browser. The aim of cloaking is to deceive search engines into displaying the page that it otherwise would not display.
1. Use SEO SpyGlass to check your backlink profile for penalty risks.
Download SEO SpyGlass
2. Avoid black-hat link-building. You probably missed our renovation of LinkAssistant aimed specifically for link-building purposes. The tool now has an upgraded link checker in-built right in there with the most popular link-building techniques highlighted as specific methods. Consult our link-building guide describing the worst and the best link-building techniques for 2021.
Download LinkAssistant
3. Observe Google Webmaster guidelines to ensure that you don't have bad linking practices in your website's link profile.

Launched: Mid-August, 2021
Rollouts: Google keeps refining it
Goal: Provide more relevant search results to user queries
On August 24, Google confirmed the page titles update with which titles in search results might be replaced by a different text from the web page. SEOs know that Google had been making minor changes to titles before, something like appending the brand name to the title. With this update, the title may be totally replaced by an H1 tag. Besides HTML tags, when generating a new title for the SERP, Google may also consider other important text on the page, as well as text anchors on the links pointing at the page.
We researched our own titles as well and found out that Google had changed titles that were too short, by appending the brand name (which coincided with the domain name). For too-long titles, it used H1 tags, which could also be cut and had the company name appended.
Besides, there are several punctuation marks to avoid in the title, namely colon, dash, and vertical bar. There are several tweaks how to speed up your on-page analysis in WebSite Auditor.
1. Find too-long titles. In Site Audit > On-page section you’ll see a warning about too-long titles.
Download WebSite Auditor
2. Rewrite titles and H1. You can also run a page-by-page audit of your pages’ titles and headlines together, and see what your competitors have for the same topic. Check your pages in Page Audit > Content Audit module.
Download WebSite Auditor
Besides, you can currently have a quick overview of all your titles and H1 headings in the Pages > All pages tab (activate the column from the Edit visible columns button and check all headings).
Download WebSite Auditor
We advise keeping your titles within a reasonable limit (for our site it was 55 – 60 characters, but the character count may be different for a different domain), not keyword-stuffed, and no explanatory punctuation in them.
Google keeps refining the algorithm and has started a feedback thread for the page titles update.

Launched: July 26, 2021
Rollouts: Two weeks onward
Goal: Improve search results and reduce the effectiveness of deceptive link building techniques
This summer is hot for updates. On July 26, Google announced a link spam update. Although Google proudly reports that over the decade the effectiveness of link schemes has decreased, search engineers still observe sites intentionally building spammy links to manipulate ranking.
The update is aimed to fight link spam and reward sites with high-quality content and good user experience. As part of their ongoing effort to fight link spam, Google may hand out both algorithmic and manual actions if a site is caught red-handed on link schemes. That is why we suggest the following steps to secure your site against link penalty.
1. Check your site's link profile for low-quality links with SpyGlass backlink checker. If you notice a massive flow of low-quality backlinks, ask the webmasters of the linking domains to take them down.
2. If the linking site owners keep silent and don't remove the harmful backlinks, use the disavow tool to tell Google not to consider these links. Disavowed links will not harm your rankings.
3. Try to use white-hat link building practices only. Consult our comprehensive guide on how to do link building SEO with SEO PowerSuite. And here are a few tips about link-building tools and tactics that are still legal and actionable.
4. Take care of your outbound links as well. If you have sponsored content or affiliate links on your site, mark them with rel="sponsored" attribute.

On June 24, Google reported on the release of the spam update within their regular work to improve search results.
According to the reports, Google constantly improves AI algorithms to remove online scam from top results. The algorithms detect 40 billion spammy pages each day. Such pages pose a threat to online security because they may install malware and steal users' private data. Google claims that over several years, it decreased the amount of automatically generated or scraped content by 80%. Among other factors, it detects and thwarts such black-SEO techniques as:
To stay on the safe side, follow webmaster guidelines to ensure the security and credibility of your pages. Use Search Console to monitor the security status. You may get a notice in the Console once someone compromises your site security.
And remember that it's easier to prevent hacking than recover from it. So use the best practices to protect your site's security.

The Page Experience update was planned to roll out gradually, to ensure that no serious unintended issues happen. The update considers several page experience signals, including the three Core Web Vitals metrics: loading speed, visual stability and interactivity.
Besides, the Top Stories carousel feature on Google Search include all news content that meets the Google News policies criteria. It means that, to appear in Google news, it won't be required any longer to have AMP pages, the same as to have the highest Core Web Vitals score. The AMP badge will also be removed from AMP content.
Google expects that the Page Experience Update will not make drastic changes to rankings. However, it introduced a new tool to safeguard sites' positions through page experience checks. The new Page Experience Report in Search Console checks the following factors:
And one more how-to from the WebSite Auditor.
Anticipating the Page Experience Update, WebSite Auditor team added the checkup feature for Core Web Vitals metrics.
Step 1. Launch the WebSite Auditor with your site project.
Step 2. Get the Page Speed Insights API, it's free and allows checking 25 000 pages a day.
Step 3. Start the task to run CWV check. Analyze this.
The Page Speed Insights report provides Lab data (ideal simulated stats how your site performs) and Field data (how users interacted with your pages over almost a month). While you enter the exact page in the Page Speed Insights tool and check page by page, in WebSite Auditor you will be able to analyze the pages in bulk, filtering all pages by values and factors.

Google reported it was a regular Core update that happens several times a year. This one is the first in a two-series update, the second part is planned to take place in July. As the 10-day update was over, there were mixed reports on SERPs fluctuation and rankings change. The second part of the update may probably reverse the impact of the June changes.
Nothing in this algorithm update was site-specific. Google referred to its regular guidance for core algorithm updates.

On April 8, 2021 Google announced sharing an improvement to its ranking systems aimed to better reward product reviews, initially for the English language. The problem behind this one update is the abundance of thin-content product reviews that bring little value to users. This improvement is expected to improve ranking of rich content product reviews.
The safeguard against the Product Reviews Update is following general quality guidelines: reviews should be based on original research and insightful analysis from experts or enthusiasts who know the topic well. Google lists several questions to help you produce a high-quality review that shouldn't be vulnerable to this ranking improvement. For example, a good review covers pros and cons of the product, provides descriptive samples, measurements, and addresses issues that influence buyer decision. Briefly, no hackwork, write in-depth and comprehensive reviews.

The Passage Ranking update was announced in November 2020 and launched on February 10, 2021 for the English laguage, with full rollouts expected shortly. Google promised that the update would affect only 7% of all queries.
The Passage Ranking was aimed to help long-form pages to rank with some parts of its content. Google did not share any specific guidlines to optimize for the update. The advice was just to keep focusing on great content. SEOs registered only slight volatility on SERPs, stating the impact was minimal.
Passage Ranking was a change in the ranking mechanism and did not introduce any new type of search result features. With this update, you may want to pay some more attention to headings and paragraphs, the semantic and structure of covering subtopics within a bigger topic. Although, the algorithm is expected to have the job well-done in any case.

On December 3, 2020 Google rolled out a broad core algorithm update, as it does several times per year. Many SEOs noticed SERPs volatility yet on December 1, though it might be unrelated. And the main question discussed in the aftermath has been: why Google rolled out such a massive update right on holiday shopping season?
The impact so far stays unclear, with various domains reporting equally many gains or losses. Google guidance about such algorithm updates remains as covered before (please check E-A-T quality guidelines).

Actually, Google adds search algorithm changes somewhat daily and officially confirms only major algorithm updates that might affect SERPs significantly (which happen several times a year). Google confirmed its major core algorithm update on January 13, 2020, and one of the latest updates rolled out on May 4.
As a quick tip, you can guess that some update has taken place from the keyword fluctuation graph in Rank Tracker’s SERP Analysis.
Go to Target Keywords > Rank Tracking, click on the SERP Analysis tab in the lower screen, and switch to the Graph view. You need to click on the Record SERP data button for every project you'd like to see the SERP fluctuation graph (the feature is available only in paid version of Rank Tracker).
An average daily fluctuation is about 6.3%. Red spikes indicate that the SERP has changed significantly on that day, probably because of some algorithmic updates.
Typically, there’s no strict explanation how exactly the Google algorithm changes may affect your site. That’s why there is nothing particular to fix quickly. The Google Webmasters advised us to focus on quality and provided a checklist on how to keep your site content in line with their guidelines. Briefly, sites should provide original, up-to-date high-quality content that brings real value to users.
Our recent survey among SEO experts revealed that with every new core update, people do nothing but monitor ranking stats. And if a site got penalized, they fix traditional SEO factors, with a focus on content and links. Again, WebSite Auditor comes to your rescue explaining how to improve content and keep your site free from SEO errors.

Launched: January 22, 2020
Goal: Prevent URLs in featured snippets to appear twice on the first page of organic search results
Google rolled out this change on January 22, 2020 which caused a bit of a fuss with SEOs that’s been finally systematized here.
What used to be called a position zero in the search engine results is now the first position. It’s up to you whether you want to get into the featured snippet or want to appear somewhere among 2 to 10 results. This ranking algorithm update has occurred one-time and affected 100% of results.
It still makes sense to monitor what pages are ranking with rich snippets and for what keywords. You can use the Rank Tracker tool to record a history of SERPs and to receive an alert when your site gets into a featured snippet for a certain keyword. In the Target Keywords module go to Ranking Keywords > Ranking Progress tab, and switch to the Rank Progress > Rank History tab.

Launched: July 1, 2019
Rollouts: Onward until September 2020
Goal: As most users now search on Google from mobile devices, Googlebot primarily crawls and indexes pages with the smartphone user-agent going forward
Starting from July 1, 2019, mobile-first indexing was enabled by default for all new websites. For older or existing websites, Google continued to monitor and evaluate pages; full mobile-first indexing has been enabled since September, 2020.
Mobile-first indexing implies that most of the crawling is conducted by mobile smartphone user-agent, though, occasionally the traditional desktop Googlebot will crawl sites as well.
It means that most of the information that appears in search comes from mobile versions of sites. One of the recommended approaches is to use responsive design for newly launched websites instead of a separate mobile version. If you still choose to serve separate site versions, make sure that information is consistent in both desktop and mobile, i.e.: content, images, links are the same; meta data are the same (titles, meta descriptions, robots text); structured data are consistent.
And certainly, audit your site and fix errors, such as duplicate issues, restricted or blocked content, missing alt texts, low quality images, and page speed issues. You can check out the best practices for mobile-first indexing from Google, as well as audit your site with WebSite Auditor.

Launched: October 25, 2019
Rollouts: December 9, 2019
Goal: Helps the search engine to understand context, especially in spoken queries
BERT is a deep-learning technique created for natural language processing: the Google algorithm is set to interpret natural language and understand context based on pre-training from a body of text on the web. This technique inside the ranking algorithm was particularly needed since the spread of voice search assistants. Google named BERT as “one of the biggest leaps in the last five years”.
Google rolled out its first BERT update for the English language, and then for over 70 other languages. Earlier reports said it had affected 10% of all search queries.
Actually, there isn’t much to be worried about BERT, the safeguards are the same as those applied with Hummingbird and RankBrain. Just provide high-quality content that answers user queries in the most proper form.
The search algorithm was aimed not to get sites penalized, but rather to boost the ones that fit better user queries. Are there any tweaks here? First, use long-tail research to explore your users’ intent. Second, examine the top 10 on the SERPs in order to understand user intent for those keywords, and what your competitors do to have their pages rank in top.
Go for long-tail keywords with Related Questions research method, including People Also Ask and Question Autocomplete forms. You’ve got to research more conversational keywords. Optimize your pages so that to meet users’ quest behind those keywords as fully as possible. It is recommended to use natural language, for example, in the form of questions in a FAQ section. This raises your chances to compete for top search rankings and even a featured snippet.
Check out our latest video for beginner-friendly tips and tools.
To comply with BERT and other major algorithms related to natural language, you’ve got to improve your page's scope and relevance. The best way to do it is with the help of the Content Editor and TF-IDF analysis tools that are integrated in WebSite Auditor. Certainly TF-IDF is a bit old language model, I mean it works differently from BERT. However, it can be a good clue for your optimization. It allows you to extract keywords by analyzing top 10 of your competitors and collecting keywords that they have in common.
Move to Content Analysis > TF-IDF, enter the URL to analyze in the Pages search bar in the upper left corner, and see how your keyword usage compares to competitors' on the TF-IDF chart. The tool will provide a suggestion if you should use more or less of the keyword in your text.

Launched: August 2019
Goal: Improve search results by more appropriate match with user intent, especially for businesses dealing with people’s wellbeing (health, fitness, and finance)
Google Medic update was named this way when SEOs saw what types of sites were affected by these Google algorithm changes – mainly health and fitness websites, but not only. Since it was rolled out in the first week of August, a heavy flux was noted in search rankings for business sites, as well. Google did not go much into details, saying it was just a core update, and no fix for it was needed. The most shared guess is that the change was aimed to match pages with their types of intent.
When Google rolled out this update, the affected sites had to take really hard efforts to recover. Since that point, concerns of user intent have become more relevant than ever. Just have in mind three types of queries that imply a certain intent: informational (what/where/how), investigational (compare/review/kinds of) and transactional (order/get/buy). You’ve got to dive a bit into long-tail keyword research to find out what users are looking for on your pages, and optimize them accordingly.
Use Rank Tracker’s Keyword Research module to mine your best keyword opportunities. Once you have them all collected in the Keyword Sandbox, use filters to group them according to intent and other important metrics, then add to your Keyword Map where you can map each keyword, or a group of keywords, to a certain landing page. Use tags and notes to mark which pages are transactional and which are informational.

Launched: July 9, 2018
Goal: Boosts faster mobile pages
Google began updating its search algorithm towards mobile experience long before, so what makes this one special? Google officially confirmed that, starting with speed algorithm updates, page speed became a ranking factor for mobile pages.
First, check your mobile pages for load speed. For this purpose, use the PageSpeed Insights from Google, Lighthouse, or Mobile Friendly Test. You can find the latter integrated in Website Auditor software.
When you spot slow page issues, you can find the cause by looking deeper into your files with a Website Auditor check. Go to Pages > All Resources > Internal Resources, and filter them by Speed and Server Response Time. Here you will see what resources might need resizing, compression etc.
Besides, the latest of Google's updates concerned the Core Web Vitals, a bunch of user experience factors that are going to become part of the ranking algorithm somewhat next year. Loading speed and user interactivity is among them. So, it certainly makes sense to prepare for future Google algorithm changes by improving your site speed and user engagement.

Launched: March 8, 2017
Rollouts: —
Goal: Filter out low quality search results whose sole purpose is generating ad and affiliate revenue
Fred algorithm got its name from Google's Gary Illyes, who jokingly suggested that all algorithm updates be named "Fred". Google confirmed the update took place, but refused to discuss the specifics of it, saying simply that the sites that Fred update targets are the ones that violate Google's webmaster guidelines. However, the studies of Fred-affected sites show that the vast majority of them are content sites (mostly blogs) with low-quality articles on a wide variety of topics that appear to be created mostly for the purpose of generating ad or affiliate revenue.
1. Review Google's guidelines. This may seem a tad obvious, but reviewing the Google Webmaster guidelines and Google Search Quality Guidelines (particularly the latter) is a good first step in keeping your site safe from Fred algorithm penalties.
2. Watch out for thin content. Look: New York Times, the Guardian, and Huffington Post all show ads — literally every publisher site does. So it's not the ads that Fred algorithm targets; it's the content. Audit your site for thin content, and update the low quality, low-word-count pages with relevant, useful information.
To start the check, navigate to the Pages module in SEO PowerSuite's WebSite Auditor and look for the Word count column. Now, sort the pages by their word count by clicking on the column's header to instantly spot pages with too little content.
But remember: short pages can do perfectly fine for certain queries. To see if your content length is within a reasonable range for your target keywords, go to Content Analysis and select the page you'd like to analyze. Enter the keyword, and hang on a sec while Google examines your and your top ranking competitors' pages. When the analysis is complete, look at Word count in body. Click on this factor and see how long the competitors' pages are.
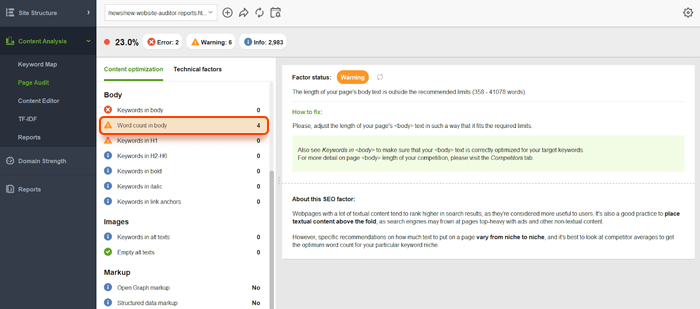
To see each individual competitor's content length, click on Keywords in body and switch to Competitors. Here, you'll get a list of your top 10 competitors for the keywords you specified, along with the total word count on each of these pages. This should give you a solid idea on approximately how much content the searchers are looking for when they search for your target keywords.

Launched: September 1, 2016
Rollouts: —
Goal: Deliver better, more diverse results based on the searcher's location and the business' address
The Possum update is the name for a number of recent algorithm changes in Google's local ranking search filter. After the Possum update, Google returns more varied results depending on the physical location of the searcher (the closer you are to a certain business physically, the more likely you'll see it among local results) and the phrasing of the query (even close variations now produce different results). Somewhat paradoxically, Possum also gave a boost to businesses that are outside the physical city area. (Previously, if your business wasn't physically located in the city you targeted, the search engine hardly ever included it into the local pack, it was hardly ever included into the local pack; now this isn't the case anymore.) Additionally, businesses that share an address with another business of a similar kind may now be deranked in the search results.
1. Do geo-specific rank tracking. After Possum, the location from which you're checking your rankings plays an even bigger part in the results you get. If you haven't done this yet, now is the time to set up a a search filter with a custom location to check positions from in SEO PowerSuite's Rank Tracker. To get started, open the tool, create a project for your site, and press Add search engines at Step 4. Next to Google (or Google Maps, if that's what you're about to track), click Add Custom. Next, specify the Preferred location (since Possum made the searcher's location so important, it's best to specify something as specific as a street address or zip code):
You can always modify the list of the local search engines you're using for rank checking in Preferences > Preferred Search Engines.
2. Expand your list of local keywords. Since Possum resulted in greater variety among the results for similar-looking queries, it's important that you track your positions for every variation separately.
To discover those variations, open SEO PowerSuite's Rank Tracker and create or open a project. Go to the Keyword Research module and click Suggest keywords. Enter the localized terms you are already tracking and hit Next. Select Google Autocomplete as your research method.
This should give you an ample list of terms that are related to the original queries you specified. You may also want to repeat the process for other methods, particularly Google Related Searches and Google Trends for even more variations.
Overall, with the Possum update, it's becoming even more important to optimize your listings specifically for local search. For a full list of local ranking factors and how-to tips, jump here.

Launched: October 26, 2015 (possibly earlier)
Rollouts: —
Goal: Deliver better search results based on relevance & machine learning
RankBrain is a machine learning system that helps Google better decipher the meaning behind queries, and serve best-matching search results in response to those queries.
While there is a query processing component in RankBrain, there also is a ranking component to it (when RankBrain was first announced, Google called it the third most important ranking factor). Presumably, RankBrain can somehow summarize what a page is about, evaluate the relevancy of search results, and teach itself to get even better at it with time.
The common understanding is that RankBrain, in part, relies on the traditional SEO factors (links, on-page optimization, etc.), but also looks at other factors that are query-specific. Then, it identifies the relevance features on the pages in the index, and arranges the results respectively in SERPs.
1. Maximize user experience. Of course, RankBrain isn't the reason to serve your visitors better. But it's a reason why not optimizing for user experience can get you down-ranked in SERPs.
Keep an eye on your pages' user experience factors in Google Analytics, particularly Bounce Rate and Session Duration. While there are no universally right values to stick by, here are the averages across various industries reported by KissMetrics (you can find the complete infographic here.
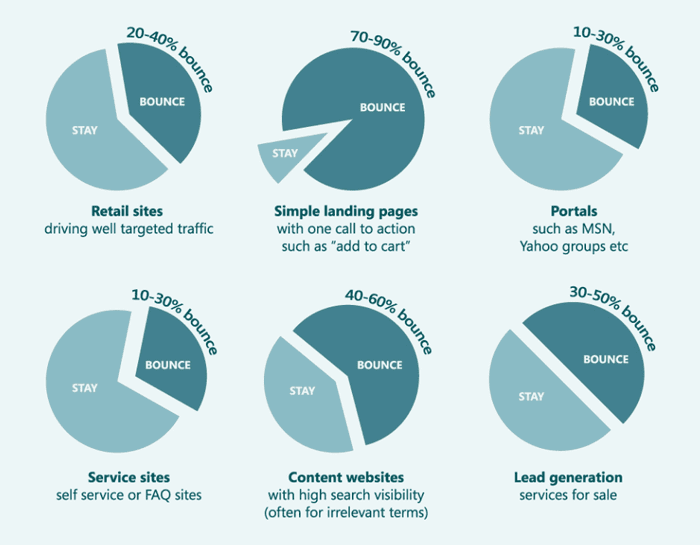
If your bounces for some of the pages are significantly above these averages, those are the low-hanging fruit to work on. Consider A/B testing different versions of these pages to see which changes drive better results.
As for session duration, keep in mind that the average reading speed (for readers who skim) is 650 words per minute. Use this as guidance in assessing the amount of time visitors spend on your pages, and see if you can improve that by diversifying your content, such as including more images and videos. Additionally, examine the pages that have the best engagement metrics, and use takeaways in crafting your next piece of content.
2. Do competition research. One of the things RankBrain is believed to do is identify query-specific relevance features of web pages, and use those features as signals for ranking pages in SERPs. Such features can be literally anything on the page that can have a positive effect on user experience. To give you an example, pages with more content and more interactive elements may be more successful.
While there is no universal list of such features, you can get some clues of what they may be by analyzing the common traits of your top ranking competitors. Start SEO PowerSuite's Rank Tracker and go to Preferences > Competitors. Click Suggest, and enter your target keywords (you can — and should — make the list long, but make sure you only enter the terms that belong to one topic at a time). Rank Tracker will now look up all the terms you entered and come up with 30 sites that rank in Google's top 30 most often. When the search is complete, choose up to 10 of those to add to your project, examine their pages in-depth, and look for relevance features you may want to incorporate on your site.


Launched: April 21, 2015
Rollouts: —
Goal: Give mobile friendly pages a ranking boost in mobile SERPs, and de-rank pages that aren't optimized for mobile
Google's Mobile Friendly Update (aka Mobilegeddon) was meant to ensure that pages optimized for mobile devices rank at the top of mobile search, and subsequently, down-rank pages that were not mobile friendly. Desktop searches have not been affected by the update.
The Mobile-Friendly Update applied at page-level, meaning that one page of your site can be deemed mobile friendly and up-ranked, while the rest might fail the test. The Mobile-Friendly Update was one in a row of ranking algorithms that worked together in a bunch, and if a certain page ranked high thanks to its great content and user engagement, the Mobile-Friendly Update did not affect it a lot.
1. Go mobile, cap. There are a few mobile website configurations to choose from, but Google's recommendation is responsive design. Google also has specific mobile how-tos for various website platforms to make going mobile easier for webmasters.
The Mobile-Friendly Update became the first in the series of Google algorithm changes towards mobile-first indexing. Starting from July 1, 2019, for all new sites, the search engine sends its mobilebot forward, so if you are launching a new site, be ready to meet it with mobile-friendly pages.
2. Take the mobile friendly test. Going mobile isn't all it takes — you must also pass Google's mobile friendliness criteria to get up-ranked in mobile SERPs. Google's mobile test is integrated into SEO PowerSuite's WebSite Auditor, so you can check your pages' mobile friendliness quickly.
Launch WebSite Auditor and open your project. Go to Content Analysis and click Add page to pick a page to be analyzed. Enter your target keywords and give the tool a moment to run a quick page audit. When the audit is complete, switch to Technical factors on the list of SEO factors on the left, and scroll down to the Page usability (Mobile) section.
The Mobile friendly factor will show you whether or not your page is considered mobile friendly overall; here, you also get a mobile preview of your page. The factors below will indicate whether your page meets all of Google's mobile friendliness criteria. Click on any factor with an Error or Warning status for specific how-to fix recommendations.
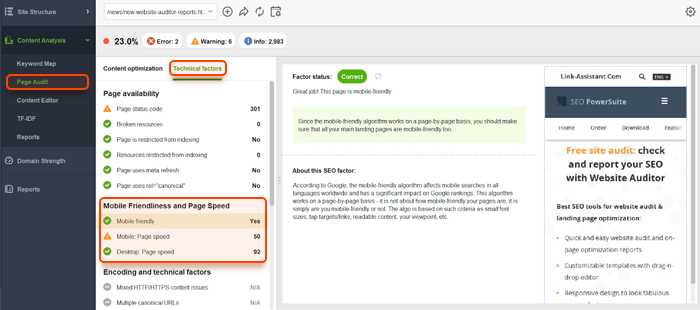

Launched: July 24, 2014 (US)
Rollouts: December 22, 2014 (UK, Canada, Australia)
Goal: Provide high quality, relevant local search results
Google Pigeon (initially tried on English only) dramatically altered the results Google returns for queries in which the searcher's location plays a part. According to Google, Pigeon created closer ties between the local algorithm and the core search algorithm, meaning that the same SEO factors are now being used to rank local and non-local Google results. This update also uses location and distance as a key factor in ranking the results.
Pigeon led to a significant (at least 50%) decline in the number of queries local packs are returned for, gave a ranking boost to local directory sites, and connected Google Web search and Google Map search in a more cohesive way.
1. Optimize your pages properly. Pigeon brought in the same SEO criteria for local listings as for all other Google search results. That means local businesses now need to invest a lot of effort into on-page optimization. A good starting point is running an on-page analysis with SEO PowerSuite's WebSite Auditor. The tool's Content Analysis dashboard will give you a good idea about which aspects of on-page optimization you need to focus on (look for the factors with the Warning or Error statuses). Whenever you feel like you could use some inspo, switch to the Competitors tab to see how your top ranking competitors are handling any given part of on-page SEO.
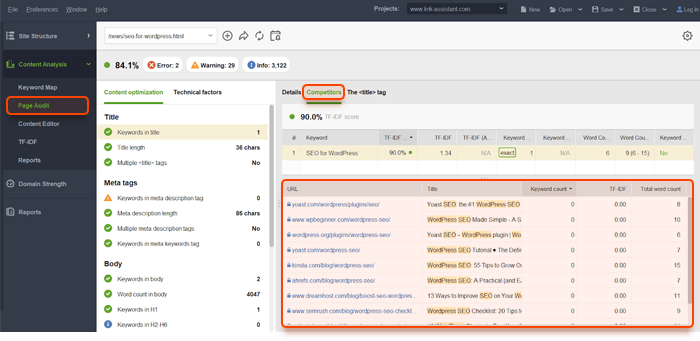
For a comprehensive guide to on-page optimization, check out the on-page section of SEO Workflow.
2. Set up a Google My Business page. Creating a Google My Business page for your local biz is the first step to being included in Google's local index. Your second step will be to verify your ownership of the listing; typically, this involves receiving a letter from Google with a pin number which you must enter to complete verification.
As you set up the page, make sure you categorize your business correctly — otherwise, your listing will not be displayed for relevant queries. Remember to use your local area code in the phone number; the area code should match the code traditionally associated with your location. The number of positive reviews can also have an influence on local search rankings, so you should encourage happy customers to review your place.
3. Make sure your NAP is consistent across your local listings. The Google search engine will be looking at the website you've linked to from your Google My Business page and cross-reference the name, address and phone number of your business. If all elements match, you're good to go.
If your business is also featured in local directories of any kind, make sure the business name, address, and phone number are also consistent across these listings. Different addresses listed for your business on Yelp and TripAdvisor, for instance, may put your local rankings to nowhere.
4. Get featured in relevant local directories. Local directories Yelp, TripAdvisor and the like, have seen a major ranking boost after Pigeon update. So while it may be harder for your site to rank within the top results now, it's a good idea to make sure you are featured in the business directories that will likely rank high. You can easily find quality directories and reach out to webmasters to request a feature with SEO PowerSuite's link building tool, LinkAssistant.
Launch LinkAssistant and open or create a project for your site. Click Look for prospects in the top left corner and pick Directories as your research method.

Enter your keywords — just as a hint, specify category keywords plus your location (e.g. "dentist Denver") — and give the tool a sec to find the relevant directories in your niche.
In a minute, you'll see a list of directories along with the webmasters' contact email addresses. Now, pick one of the directories you'd like to be included in, right-click it, and hit Send email to selected partner. Set up your email prefs, compose the message (or pick a ready-made email template), and send it off!

Launched: August 22, 2013
Rollouts: —
Goal: Produce more relevant search results by better understanding the meaning behind queries
Google Hummingbird is a major algorithm change that deals with interpreting search queries, (particularly longer, conversational searches) and providing search results that match searcher intent, rather than individual keywords within the query. The name of the Google algorithm was derived from comparing it to the accuracy and speed of the hummingbird.
While keywords within the query continue to be important, Hummingbird adds more strength to the meaning behind the query as a whole. The use of synonyms has also been optimized with Hummingbird; instead of listing results with the exact keyword match, the Google algorithm shows more theme-related results in the SERPs that do not necessarily have the keywords from the query in their content.
1. Expand your keyword research. With Hummingbird, you need to focus on related searches, synonyms and co-occurring terms to diversify your content, instead of relying solely on short-tail terms you'd get from Google Ads. Great sources of Hummingbird-friendly keyword ideas are Google Related searches, Google Autocomplete, and Google Trends. You'll find all of them incorporated into SEO PowerSuite's Rank Tracker.
To start expanding your list of target keywords, open Rank Tracker and create or open a project. Enter the seed terms to base your research upon, and hit to search. In the next step, go to the Keyword Research module and check your ranking keywords first. Then, one by one, explore your potential keywords for ranking with all available keyword research methods. For example, select the Relates Searches method, add your topic keywords and hit Search.
Hang on while Rank Tracker is pulling suggestions for you, and when it's done all the keyword ideas will be in the Sandbox, from where you can pick those that deserve to be added to your rank tracking list. Then go through the process again, this time selecting Google Autocomplete Tools as your research method. Do the same for Related questions. Next, proceed with analyzing the keywords' efficiency and difficulty, and pick the top terms to map them to landing pages.
2. Discover the language your audience uses. It's only logical that your website's copy should be speaking the same language as your audience, and Hummingbird is yet another reason to step up the semantic game. A great way to do this is by utilizing a social media listening tool (like Awario) to explore the mentions of your keywords (your brand name, competitors, industry terms, etc.) and see how your audience is talking about those things across social media and the Web at large.
3. Ditch exact-match, think concepts. Unnatural phrasing, especially in titles and meta descriptions, is still popular among websites, but with search engines' growing ability to process natural language, it can become a problem. If you are still using robot-like language on your pages for whatever reason, with the Hummingbird update (or, to be honest, four years before) is the time to stop.
Including keywords in your title and description still matters; but it's just as important that you sound like a human. As a nice side effect, improving your title and meta description is sure to increase the clicks your Google listing gets.
To play around with your titles and meta descriptions, use SEO PowerSuite's WebSite Auditor. Run the tool, create or open a project, and navigate to the Pages module. Go through your pages' titles and meta descriptions and spot the ones that look like they were created purely for search engine bots. When you spot a title you'd like to correct, right-click the page and hit Analyze page content. The tool will ask you to enter the keywords that you want your page to be optimized for. When the analysis is complete, go to Content Editor, switch to the Title & Meta tags tab, and rewrite your title and/or meta description. Right below, you'll see a preview of your Google snippet.

Launched: Aug 2012
Rollouts: Oct 2014
Goal: De-rank sites with copyright infringement reports
Google's Pirate Update was designed to prevent sites that have received numerous copyright infringement reports from ranking well in Google search. The majority of sites affected are relatively big and well-known websites that made pirated content (such as movies, music, or books) available to visitors for free, particularly torrent sites. Despite this effort, some of the best torrent downloaders continue to be popular among users. That said, it still isn't in Google's power to follow through with the numerous new sites with pirated content that emerge literally every day.
Don't distribute anyone's content without the copyright owner's permission. Really, that's it.

Launched: April 24, 2012
Rollouts: May 25, 2012; Oct 5, 2012; May 22, 2013; Oct 4, 2013; Oct 17, 2014; September 27, 2016; October 6, 2016; real-time since
Goal: De-rank sites with spammy, manipulative link profiles
Google Penguin update aimed to identify and down-rank sites with unnatural link profiles, deemed to be spamming the search results by using manipulative link tactics. Google rolled out Penguin algorithm updates once or twice a year until 2016, when Penguin became part of Google's core ranking algorithm. Now it operates in real time, which means that the algorithm penalties are applied faster, and recovery also takes less time.
1. Monitor link profile growth. Google isn't likely to penalize a site for one or two spammy links, but a sudden influx of toxic backlinks could be a problem. To avoid getting penalized by Google Penguin updates, look out for any unusual spikes in your link profile, and always look into the new links you acquire. By creating a project for your site in SEO PowerSuite's SEO SpyGlass, you'll instantly see progress graphs for both the number of links in your profile, and the number of referring domains. An unusual spike in either of those graphs is a reason enough to look into the links that your site suddenly gained in order to secure it from a Google penalty.
2. Check for penalty risks. The stats that Penguin update likely looks at are incorporated into SEO SpyGlass and its Penalty Risk formula, so instead of looking at each individual factor separately, you can weigh them as a whole, pretty much like the Google algorithm does.
In your SEO SpyGlass project, switch to the Linking Domains dashboard and navigate to the Link Penalty Risks tab. Select all domains on the list, and click Update Link Penalty Risk. Give SEO SpyGlass a minute to evaluate all kinds of quality stats for each one of the domains. When the check is complete, examine the Penalty Risk column, and make sure to manually look into every domain with a Penalty Risk value over 50%.
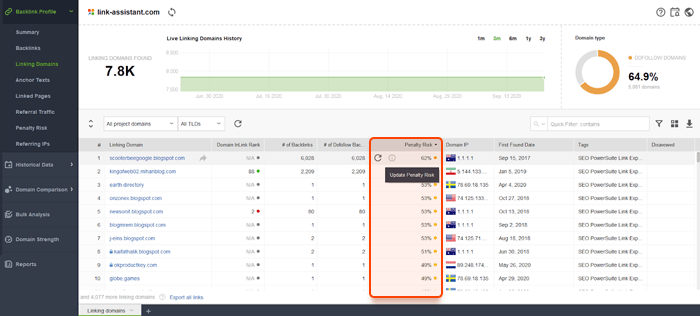
If you use SEO SpyGlass' free version, you'll get to analyze up to 1,000 links; if you're looking to audit more links, you'll need a Professional or Enterprise license.
3. Get rid of harmful links. Ideally, you should try to request removal of the spammy links in your Google profile by contacting the webmasters of the linking sites. But if you have a lot of harmful links to get rid of, or if you don't hear back from the webmasters, the only remedy you have is to disavow the low-quality links using Google's Disavow tool. This way, you'll be telling Google spider to ignore those links when evaluating your link profile. Disavow files can be tricky in terms of syntax and encoding, but SEO SpyGlass can automatically generate them for you in the right format.
In your SEO SpyGlass project, select the links you're about to disavow, right-click the selection, and hit Disavow backlinks. Select the disavow mode for your links (as a rule of thumb, you'd want to disavow entire domains rather than individual URLs). Once you've done that for all harmful links in your project, go to Preferences > Blacklist/Disavow backlinks, review your list, and hit Export to save the file to your hard drive. Finally, upload the disavow file you just created to Google's Disavow tool.
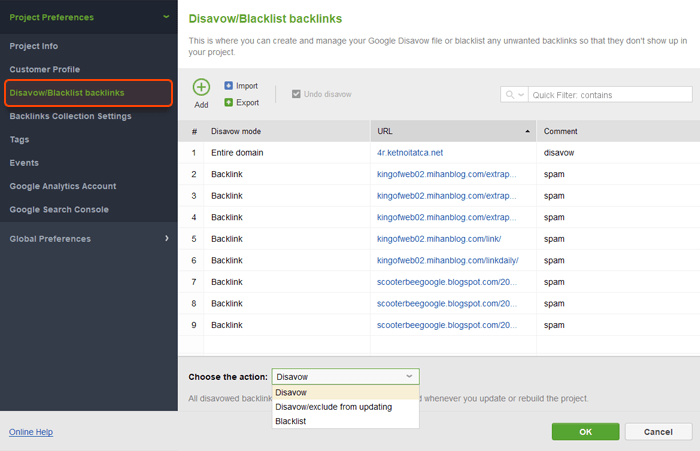
Since it’s become a core ranking algorithm, one cannot say for sure that a Penguin update happens on this or that day. If you notice that your site authority or visibility has dropped, it can be a signal that the site has been penalized by Penguin. Likewise, one cannot say exactly when the full recovery takes place after all harmful links are removed. Positive effects should take place yet with the next Google spider crawl. However, you cannot expect the site authority to return straight to its previous level, since it’d been bloated with artificial links. You’ll need to apply some more accurate link-building tactics.
Sometimes sites get hit by a manual Google penalty rather than a Penguin algorithm sanction. This happens when human reviewers at Google notice manipulative tactics on a site that have gone unnoticed by a Penguin update. You will receive a notice about a manual Google penalty under the Manual Actions tab in the Search Console. Your actions here follow a similar recovery path: go to remove or disavow the bad backlinks and ask Google to reconsider the manual action.
For a more detailed guide on conducting a Penguin-proof link audit, jump here.

Launched: Feb 24, 2011
Rollouts: ~monthly
Goal: De-rank sites with low-quality content
Google Panda is an algorithm used to assign a content quality score to webpages and down-rank sites with low-quality, spammy, or thin content. Initially, Panda update was a search filter rather than a part of Google's core algorithm, but in January 2016, it was officially incorporated into the ranking algorithm. While this doesn't mean that Panda is now applied to search results in real time, it does indicate that both getting filtered by and recovering from Google Panda now happens faster than before.
1. Check for duplicate content across your site. Internal duplicate content is one of the most common triggers for Google Panda update, so it's recommended that you run regular site audits to make sure no duplicate content issues are found. You can do it with SEO PowerSuite's Website Auditor (if you have a small site with under 500 resources, the free version should be enough; for bigger websites, you'll need a WebSite Auditor license).
To start the check for duplicate content, launch WebSite Auditor and create a project for your site. Hang in a moment until the app completes the crawl. When done, pay attention to the on-page section of SEO factors on the left, especially Duplicate titles and Duplicate meta descriptions. If any of those have an Error status, click on the problematic factor to see a full list of pages with duplicate titles/descriptions.
If for some reason you can't take down the duplicate pages penalized by Google Panda update, use a 301 redirect or canonical tag; alternatively, you can block the pages from Google spider indexing with robots.txt or the noindex meta tag.
2. Check for plagiarism. External duplicate content is another Panda trigger. If you suspect that some of your pages may be duplicated externally, it's a good idea to check them with Copyscape. Copyscape gives some of its data for free (for instance, it lets you compare two specific URLs), but for a comprehensive check, you may need a paid account.
Many industries (like online stores with thousands of product pages) cannot always have 100% unique content. If you run an e-commerce site, try to use original images where you can, and encourage user reviews to make your product descriptions stand out from the crowd.
3. Identify thin content. Thin content is a bit of a vague term, but it's generally used to describe an inadequate amount of unique content on a page. Thin pages are made up of duplicate content, scraped or generated automatically. Typically, thin content appears on pages with low word count that are filled with ads, affiliate links, etc., and provide little original value. If you feel that your site could be penalized by Google Panda update for thin content, try to measure it in terms of word count and the number of outgoing links on the page.
To check for thin content, navigate to the Pages module in your WebSite Auditor project. Locate the Word count column (if it's not there, right-click the header of any column to enter the workspace editing mode, and add the Word count column to your active columns). Next, sort the pages by their word count by clicking on the column's header to instantly spot the ones with very little content that risk being hit by Panda.
Next, switch to the Links tab and find the External links column, showing the number of outgoing external links on the page. You can sort your pages by this column as well by clicking on its header. You may also want to add the Word count column to this workspace to see the correlation between outgoing links and word count on each of your pages. Watch out for pages with little content and a substantial number of outgoing links.
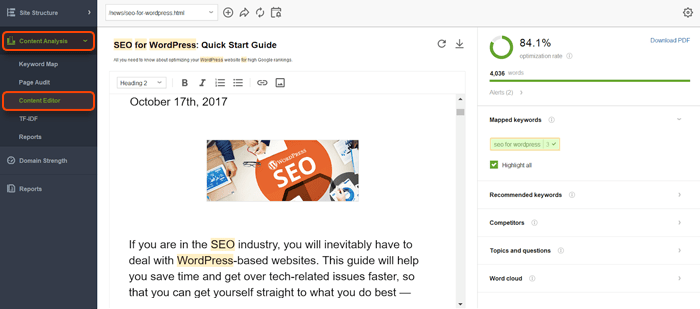
Mind that a "desirable" word count on any page is tied to the purpose of the page and the keywords that page is targeting. E.g. for queries that imply the searcher is looking for quick information ("what's the capital of Nigeria", "gas stations in Las Vegas"), pages with a hundred words of content can do exceptionally well on Google. The same goes for searchers looking for videos or pictures. But if those are not the queries you're targeting, too many thin content pages (<250 words) may get you in trouble.
As for outgoing links, Google recommends keeping the total number of links on every page under 100 as a rule of thumb. So if you spot a page with under 250 words of content and over 100 links, that's a pretty solid indicator of a thin content page.
4. Audit your site for keyword stuffing. Keyword stuffing is a term used to describe over-optimization of a given page element for a keyword. When all optimization efforts fail and your pages do not reach those desired top 10, it can be indicative of keyword stuffing issues and Google Panda update sanctions. To figure out if this is the case, look at your top ranking competitors' pages (that's exactly what SEO PowerSuite's WebSite Auditor uses in its Keyword Stuffing formula, in addition to the general SEO best practices).
In your WebSite Auditor project, go to Content Analysis, and add the page you'd like to analyze for Panda-related issues. Enter the keywords you're targeting with this page, and let the tool run a quick audit. When the audit is complete, pay attention to Keywords in title, Keywords in meta description, Keywords in body, and Keywords in H1. Click through these factors one by one, and have a look at the Keyword stuffing column. You'll see a Yes value here if you're overusing your keywords in any of these page elements. To see how your top competitors are using keywords, switch to the Competitors tab.
5. Fix the problems you find. Once you've identified the Panda-prone vulnerabilities, try to fix them as soon as you can to prevent being hit by the next Panda algorithm iteration (or to recover quickly if you've been penalized). For a small number of pages with duplicate content, use Website Auditor’s Content Editor to edit those pages right inside the module and see how the quality factor improves on the go. Go to Content Analysis > Content Editor and edit your content in either a WYSIWYG editor or HTML. Here you can play around with your titles and meta description in a user-friendly editor with a Google snippet preview. On the left, the on-page factors will recalculate as you type. Once you've made the necessary changes, hit the Download PDF button or the down-error to export the document as an HTML file to your hard drive.

If you're looking for more detailed instructions, jump to this 6-step guide conducting a content audit for Panda update issues.
Those are the major Google algorithm updates to date, along with some quick auditing and prevention tips to help your site stay afloat (and, with any luck, keep growing) in Google search.
I skipped some well-known Google algorithm updates that affected rankings one-time, and hardly any recovery could be invented. For example, in 2012, Google rolled out a filter to downgrade exact-match domains without high-quality content. Such domains proliferated for a short time when exact match for keywords was enough to rank up, a part of manipulative ranking tactics. Nothing to say about the Intrusive Interstitials back to 2015, as the Mobile-Friendly Update has made all those mobile tricks even more complicated.
So our list of Google algorithm updates is very far from exhaustive, it rather focuses on those workings of the search engine that can be uncovered with the help of SEO tools.
As always, we're looking forward to your comments and questions below. Have any of these updates had an impact on your ranks? If so, what was the tactic that helped you recover? Please share your experience in the comments!
This Google algorithm updates cheat sheet was written years ago and is being regularly revised and updated for freshness.



