Broken link
Contents
Broken link definition
A broken link is a link to a page that does not work. When a user or a search engine crawler follows such link, they see an error message or a 404 (not found) page. Another popular definition for broken links is dead links.
Why broken links appear
Broken links appear because of a variety of reasons:
- A URL was misspelled or mistyped;
- A URL structure was changed and no redirect was applied;
- A whole site is not available or timed out;
- A link points to the content (a PDF, video, Google Docs file, etc.) that is no longer available;
- A page has restricted access (password protection, firewall, etc.).
Examples of broken links
When users follow a link that is broken, they may not necessarily see a 404 (not found)[1] response code. Here are a couple of other status codes that also signalize that a link is broken:
- 400 (bad request). The host server doesn’t understand the URL on a page;
- 401 (unauthorized). A page is only available for authorized access;
- 410 (gone). A page has been removed and deindexed. Note that Google treats 410 and 404 status codes equally[1];
- This site can’t be reached. A site took too long to respond. In addition to server errors, this status may also signalize the typo in the domain name:
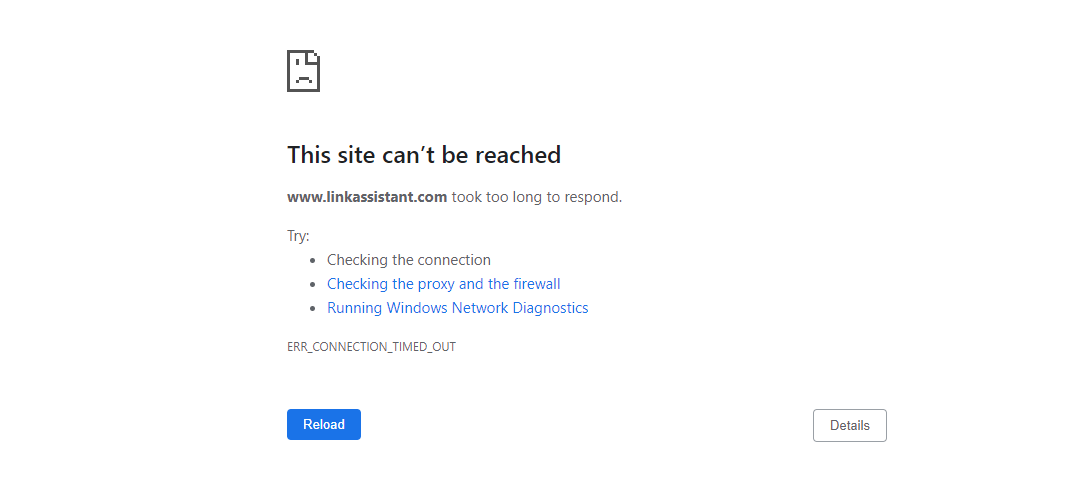
- 502 (bad gateway). A server received an invalid response because it was crushed;
- Reset. A server dropped connections because it was misconfigured or too busy.
Broken links’ meaning for SEO
Broken links themselves do not directly affect your performance in search. Still, they negatively affect both the page they are placed on and the page they link to.
Outgoing broken links
Broken links harm user experience and increase bounce rate, which will surely affect your site traffic. Besides, broken links result in incomplete content, as users cannot access the information they may need. What’s more, Google Quality Rater Guidelines say[2] that Google watches the number of broken links to determine if the site is spammy or was abandoned. And if yes, Google may start deindexing the site.
Incoming broken links
Broken links do not pass link juice, so the page where the link points to will not receive value and page strength. Plus, a page where a broken link points to may not be indexed at all if no other links point to it.
Fixing broken links
Broken links should be fixed anyway to prevent link juice drainage and poor user experience.
Broken links with 4xx status codes
Most broken links that return 4xx status codes are fixed with the help of correctly implemented 301 redirects to relevant pages. Doing so keeps users on your website (i.e. bounce rate decreases), saves link juice, and does not harm UX.
Broken links with other status codes
If a link is broken because of server issues, then it is the server that needs fixing. Make sure everything is implemented correctly on the server side and ask Google to recrawl pages.
Setting up a custom 404 page
Sometimes a page is moved without any alternative. In this case, you should not redirect users to your homepage but set up a custom 404 page. It should include some navigation links that may be interesting for users. Custom 404s are not indexed by Google and are needed to keep users on your site and decrease bounce rate.
Related links
The Ultimate Guide to Broken Link Building
Most Common Indexing Issues and How to Fix Them - 404 Not Found